Cleaning is carried out mainly in order to obtain material, that is, scraping of the uterine mucosa for histological examination. The material taken allows an accurate diagnosis to be made. The second purpose of cleansing is the removal of pathological formations in the cervix or in the uterine cavity.
Curettage is prescribed in the following cases:
- if a woman has long and very heavy menstruation with the presence of clots, intermenstrual bleeding, does not occur for a long time, as well as other conditions when ultrasound data do not allow us to establish the cause;
- changes in the mucous membrane of the uterus, indicating pathological processes;
- changes in the cervix;
- often cleaning is carried out before a planned gynecological operation.
Preparing for cleaning
If cleaning is carried out not according to an emergency indication, but in a planned manner, then the operation is performed before the onset of menstruation. This is necessary so that the process coincides with the physiological period of rejection. If you were prescribed with the removal of polyps, then the operation is performed after menstruation.
Before cleaning, a woman must pass general analysis blood, tests for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, undergo an ECG, make a coagulogram, pass a swab from the vagina for cleanliness. On the day of surgery, you must come on an empty stomach, pubic hair must be shaved off. Please bring socks, a long T-shirt, bathrobe, slippers and sanitary pads.
Curettage procedure
The woman is invited to the operating room, where she is located on the table in the form of a gynecological chair. The anesthesiologist talks about the presence of allergic reactions to medications and past illnesses. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, which lasts 15-25 minutes. After the injection of the drug into the vein, the patient falls asleep.
The doctor using a special probe penetrates the uterine cavity and measures the length of the cavity. Then dilates the cervix. The dilators are alternately inserted into the cervix, which leads to a gradual opening of the channel to a size that allows the curette to pass through. Then the mucous membrane of the cervix is cleaned with a special tool. The curette looks like a spoon with a long handle, one edge is sharpened. The sharp side is used for scraping. Scraping from the channel is placed in a separate jar.
After the end of the process, dilators are removed from the cervix. The vagina and cervix are treated with antiseptics, ice is placed on the stomach. Under the influence of cold blood vessels stop bleeding, the uterus contracts. The patient is transferred to the ward, where she gradually wakes up. After a few hours, the woman can go home.
Cleaning the uterus (curettage or curettage) is at least a very common surgical intervention. Information preparation before this manipulation will allow the patient to calm down, make sure that it is necessary and learn about all the nuances of the intervention. A woman should not be afraid of curettage, since in modern gynecology this procedure is painless, and its complications are extremely rare.
If the patient is scheduled for cleaning, there is nothing surprising in this. When scraping, you can determine various diseases uterus, remove the pathological process or stop the bleeding that exhausts the woman. Scraping is of two types:
- diagnostic;
- medical.
The main function of the uterus is to bear a fetus. The inner layer of the uterus is called the endometrium and is a protective mucous membrane. Every month, cyclical changes occur in the uterus of women of reproductive age. At the same time, the endometrium grows, preparing for the possible fertilization of the egg and its fixation. If pregnancy does not occur, then endometrial cells are rejected, accompanied by menstruation.
Cleansing the uterus for the body looks like artificially induced menstruation. To do this, using medical instruments or a vacuum system, the uppermost uterine layer is removed.
With properly performed scraping, only the functional uterine layer is removed, which is quickly restored. The basal uterine layer is not affected.
After cleaning, a layer of the endometrium (germ) remains in the uterus, which quickly grows and recovers. Recovery after cleansing occurs at the usual time for the monthly cycle.
The tissues obtained by scraping are sent for research.
What is the purpose of scraping
Usually, uterine curettage is performed for the following reasons:
- for histological examination and clarification of the proposed diagnosis;
- to remove pathologies in the cavity or cervix.
In what cases does cleaning happen for a diagnostic purpose, and in which it is done for treatment?
Diagnostic curettage is performed when:
- formations on the cervix;
- prolonged periods with clots, or bleeding outside the cycle;
- infertility of unknown cause;
- before operations in the uterine cavity;
- suspicion of oncological processes;
- after changes in the mucosa, confirmed by ultrasound and not disappeared after menstruation.
Curettage for therapeutic purposes can be performed in situations:
- polyps on the uterine mucosa that do not disappear after drug treatment;
- hyperplasia (excessive growth of the endometrium) of the endometrium (the only treatment);
- uterine bleeding (for various reasons, including those that are not clear);
- incomplete abortion;
- inflammation after an abortion or after spontaneous miscarriages;
- dissections with adhesions of the uterine walls;
- treatment of endometritis.

Contraindications
For any surgical intervention, there are general contraindications in the form of infectious diseases with high fever, acute inflammation, severe general ailments.
Curettage is also not performed for some gynecological diseases or conditions:
- normal pregnancy;
- malformations or infectious processes of the uterus;
- deforming tumors;
- less than 6 months after termination of pregnancy.
The doctor always decides about the possibility of scraping a woman.
Types of scraping
Two main types of scraping are commonly used:
- Separate. With this method, the cervical canal is first scraped, and then the uterus itself. It makes it easier to make a correct diagnosis and is often combined with hysteroscopy, when an optical device is inserted into the uterus. This method makes the procedure safe and reduces the risk of complications.
- The usual way of scraping with surgical instruments. Such manipulation is performed blindly and can damage the uterus.
- Vacuum cleaning. This is a gentle method that minimizes injuries during intervention. It is used as a method of diagnosis, treatment or during an abortion.
When to clean
It is undesirable to clean in parallel with the onset of menstruation due to the low information content of such research results.
It is also undesirable to clean the uterus at the beginning or middle of the cycle due to the friability of its mucosa and the risk of bleeding.
When cleaning at the beginning of the cycle or in its middle, there is a high probability of hormonal failure in the woman's body. After all, the growth of the uterine mucosa occurs in parallel with the growth of ovarian follicles. If at this moment the uterine mucosa is suddenly removed, then the work of the ovaries is disrupted - a contradiction occurs between the uterine and ovarian cycles.

How to prepare for scraping
Cleaning of the uterus can be performed according to emergency indications (for example, with uterine bleeding). In this case, there is simply no time to prepare for this intervention.
If scraping is carried out according to plan, then preparation for it is mandatory.
Before scraping, a woman is usually prescribed tests:
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- coagulograms (assessment of blood clotting);
- for hepatitis, HIV and syphilis;
- vaginal smear.
For scraping, a woman comes on an empty stomach, shaving her hair in the crotch. The patient is advised to limit the amount of liquid and take along pads, slippers, a disposable diaper, clean cotton items (T-shirt, socks, bathrobe).
What awaits a woman when scraping
Of course, it is important for a woman to know in advance what she should prepare for and what awaits her in the process of cleaning the uterus. Consider in general how scraping is performed.
- A woman enters the operating room and sits on a table that looks like a gynecological chair.
- The anesthesiologist clarifies the patient's possible allergic reactions and previous diseases.
- A woman is injected intravenously with drugs for anesthesia with a short-term effect. After that, she falls asleep and wakes up already in the ward. The patient does not have to endure any pain. In addition, modern drugs are not accompanied by hallucinations or severe recovery from anesthesia.
What kind of manipulations is the patient exposed to during cleaning?
- Before the operation, a gynecological speculum is inserted into the woman to expose the cervix.
- The gynecologist fixes the cervix with special forceps "bullets" to ensure its immobility at the time of the intervention.
- With the help of a probe, the specialist enters the uterus. Cervical dilators are then used until the cervix begins to skip the curette (curettage instrument). In this case, the tissues after scraping are placed in a special container.
- When using a hysteroscope (a device with a camera at the end), all uterine walls are examined. Then scraping is done. After the procedure, the hysteroscope is reintroduced to check the result. It is thanks to the hysteroscope that various pathological inclusions in the uterus (myomatous nodes, polyps, etc.) are removed. Usually, curettage lasts no more than 15-20 minutes.
- After the operation, the vagina and cervix are treated with antiseptics. Ice is placed on the woman's stomach to prevent bleeding.
The woman is transferred to the ward, where she stays for several hours. After that (or the next day), the woman is often allowed to go home.

Possible Complications
Complications after cleansing are rare. To do this, scraping must be carried out in medical institution qualified specialist.
However, cleaning is an operation and can have complications. Rare, but possible complications during curettage may be:
- exacerbations of gynecological inflammation;
- adhesions in the tissues of the uterus;
- puncture of the uterus with surgical instruments;
- neck tear;
- mucosal damage;
- leaving in the cavity of polyps, adhesions or nodes that were planned to be removed;
- hematometers (collections of blood in the uterus)
With careful manipulation, complications can almost always be avoided. Minor tissue damage after cleaning heal themselves. Only massive damage to the cervix or uterus requires surgical intervention. When inflammation or hematometers appear, drug treatment is used.
A serious complication of cleaning is too much removal of the mucosa. This condition often leads to infertility due to the inability to fix the ovum.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterus
The use of vacuum minimizes complications during interventions in the uterine cavity.
In addition to the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological diseases (hematometer, bleeding), vacuum curettage is very often performed when:
- termination of pregnancy;
- incomplete abortion;
- removal of parts of the fetal egg or placenta;
- frozen pregnancy.
Scraping with a vacuum method is carried out with special tips and a vacuum pump. At the same time, due to the negative pressure in the uterus, pathological tissues are brought out of the uterus.
The vacuum method is a safer and more gentle way of scraping. At the same time, the risk of hormonal disruptions and damage to the uterus or its cervix is minimal.
Vacuum complications are extremely rare, but they do happen. In addition to the usual complications of cleaning, a complication after vacuum curettage is an air embolism.

Behavior of a woman after scraping
After scraping, a woman usually has spotting discharge for several days, associated with hormonal changes in the body. Usually, menstruation begins in a month and may differ slightly from normal (be shorter, leaner, etc.)
Pain in the abdomen is natural after cleansing, and you should not be afraid of this. Usually, painkillers are recommended for pain in the lower abdomen.
- Avoid hypothermia and physical activity.
- Avoid high temperatures (steam rooms, baths, saunas).
- Observe the hygiene of the genitals.
- Give up sex for a month.
Doctors advise planning a pregnancy after cleaning no earlier than six months after an examination by a gynecologist.
Pregnancy immediately after curettage may result in miscarriage of the fetus or its intrauterine death.
In modern hospital conditions, a woman absolutely should not be afraid of cleaning. Thanks to this useful method, many gynecological pathologies can be identified and cured. Complications during the curettage procedure are extremely rare, and the intervention itself is painless for the patient.
Content:
How is scraping done?
The main purpose of curettage is to remove the top layer of the uterine lining that is shed during menstruation.
Curettage is carried out in the operating room, on a gynecological chair.
Cervical dilation and curettage can be very painful and uncomfortable, so this procedure is almost always performed under anesthesia, but in some cases (for example, immediately after childbirth, when the cervix is dilated), curettage can be performed without anesthesia. In most cases, an intravenous injection of special drugs is used as anesthesia during scraping, which in a few seconds introduces a woman into a state of shallow sleep and completely eliminates pain and memories of what happened during scraping.
Before scraping, the doctor inserts a dilator into the vagina, which allows you to straighten the walls of the vagina and makes the cervix visible.
Next, the doctor dilates the cervix - for this, he holds the cervix with a special tool and inserts a probe with a rounded end into the cervical canal. In order to achieve sufficient dilatation of the cervix, the doctor may remove the first probe and replace it with another one with a slightly larger diameter.
After sufficient expansion of the cervix, the doctor can perform a hysteroscopy (examination of the inner surface of the uterus using a special video camera) or proceed directly to curettage.
For scraping, a special tool (curette) is used, which resembles a small spoon with a long handle. With gentle movements of the curette, the doctor scrapes off the top layer of the uterine mucosa and collects the resulting tissues in a test tube, which will then be sent to the laboratory for histological analysis.
In general, the procedure for dilating the cervix and curettage can take up to 30-40 minutes.
In most cases, curettage is subjected not only to the uterine cavity, but also to the cervical canal. This procedure is called a separate diagnostic curettage (RDV). First, the cervical canal is subjected to curettage (cervical canal scraping), and then the uterine cavity is scraped. Materials obtained from curettage of the cervix and uterine cavity are collected separately and then subjected to histological examination as separate samples.
Why is a histological examination performed after curettage?
Histology (histological examination) is necessary in order to determine the structure of the tissues obtained during curettage. Histology is the most important part of the examination, as it is what distinguishes normal tissue from cancer or precancerous lesions. The results of histological analysis are usually ready within 10-14 days. After receiving them, you will need to meet with the doctor again or contact him in order to find out and discuss them.
What is diagnostic curettage?
Diagnostic curettage is performed to find out the cause of some of the symptoms that indicate a violation of the female genital organs. In particular, the doctor may prescribe curettage in order to establish the cause of symptoms such as:
- irregular periods, bloody issues from the vagina between two periods; (cm. possible causes of irregular periods)
- Excessively heavy, prolonged or painful menstruation; (cm. possible causes of excessively long periods)
- Bloody discharge from the vagina after menopause; (cm. )
- Difficulty conceiving a child or ;
- Suspicion of .
In such situations, curettage is used only to obtain samples of the lining of the uterus, further examination of which, with the help of histological analysis (histology), can help establish the correct diagnosis.
What is therapeutic scraping?
Curettage as the main or auxiliary method of treatment is used in case of diseases such as:
uterine fibroids
In some cases, fibroids are manifested by very heavy bleeding, which can only be stopped with the help of special drugs or after removal of the tumor.
Curettage may be used in preparation for fibroid surgery, or in combination with hysteroscopy to permanently remove fibroids.
Polyp of the uterus and cervix
Like fibroids, polyps can cause very heavy uterine bleeding during or between periods. Some polyps can turn into cancer. Curettage is performed to remove polyps (in the uterus or in the cervix), and the subsequent histological analysis helps to determine whether the polyp poses a cancer risk or not.
endometrial hyperplasia
Like uterine polyps, hyperplasia greatly increases the risk of uterine cancer and therefore requires removal with curettage.
endometritis
In some cases, for the successful treatment of endometritis, along with the appointment of antibiotics, it is necessary to carry out curettage of the uterus.
Curettage after childbirth
After childbirth, curettage may be necessary to remove the remnants of the placenta (children's place) and blood clots from the uterine cavity, which prevent the walls of the uterus from contracting and pose a threat of bleeding and infection. Curettage can be carried out immediately after childbirth or after a few days.
Also, curettage is used to terminate a pregnancy or to remove an abnormally developing or dead fetus.
Frozen pregnancy
The preservation of a dead embryo in the uterine cavity during a missed pregnancy creates a great danger to the health of a woman. For this reason, immediately after detection, a frozen pregnancy should be removed with scraping.
Curettage of the uterine cavity is prescribed for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. It allows you to identify the exact cause of some diseases and get rid of neoplasms (polyps, adhesions, etc.).
Curettage is a manipulation that boils down to the removal of the restored layer of the uterine mucosa with special instruments (curettes or vacuum aspirators).
The full procedure sounds like “separate diagnostic curettage”. “Separate” - since tissues from the wall of the cervix and the uterus itself are examined separately.
During the intervention, it is preferable to use a hysteroscope - a system for a detailed examination of the uterus.
For a better understanding of the essence of the procedure, some definitions should be disclosed:
- Scraping as such is only an instrumental manipulation, i.e., the designation of the action itself. The operation, depending on the method and purpose of the implementation, has a variety of names.
- Separate scraping includes sequential removal of the biomaterial first from the cervical canal, then from the uterine mucosa. After the operation, the removed tissue will be sent to the histological laboratory, at the same time, the neoplasm, for which the operation was scheduled, is excised.
- RDV + GS (hysteroscope) is an improved, more informative procedure. Previously, curettage was carried out mostly "blindly". The tool also allows you to examine the uterine cavity in detail for pathological formations. Excision of tissue or neoplasm is carried out at the end of the manipulation. The final stage is the doctor's assessment of the work done.

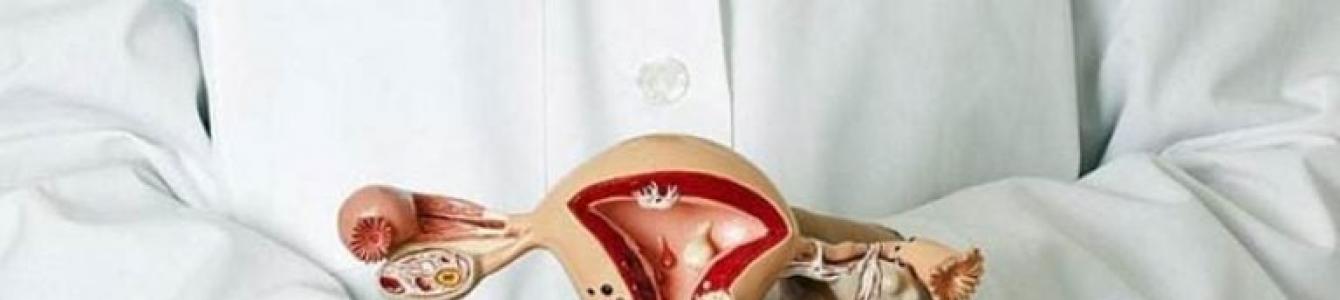
What female organ is scraped?
 The uterus is scraped. This is a hollow pear-shaped organ in which three sections are distinguished:
The uterus is scraped. This is a hollow pear-shaped organ in which three sections are distinguished:
- body- the largest part;
- isthmus- located between the body and the neck;
- neck- narrowed lower end of the uterus.
The wall of the uterus is three-layered:
- the inner layer (mucous) is the endometrium;
- the middle layer is represented by smooth muscle tissue (myometrium);
- the upper layer is serous (perimetry).
The uterus performs important functions:
- childbearing;
- menstrual;
- participates in the birth act.
Being cleaned. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that every month every non-pregnant woman of childbearing age has a rejection of the functional layer, which manifests itself in the form of menstrual bleeding. Before that, he thickens several times, thereby preparing for the adoption of a fertilized egg.
It is important for every woman who is scheduled for curettage to understand the following: as part of this procedure, only the functional layer of the endometrium is removed, which itself is rejected physiologically in each cycle. After the intervention, the mucous tissue is restored.
Together with the endometrioid tissue, neoplasms (if any) are also removed at the same time:, intrauterine adhesions, etc.
Indications for the procedure
Reading is carried out in the following cases:

Objectives of the
Curettage plays a therapeutic and diagnostic role. The collected material is subjected to histological examination, so that a correct diagnosis can be made. If pathological neoplasms or adhesions are found in the uterus, they are excised.
The procedure is widely used in the management of patients with endometrial hyperplasia in the premenopausal and postmenopausal period. Cleaning with a hysteroscope for this pathology is the initial stage of therapy.
Curettage is carried out with absolute or incomplete fusion of the uterine cavity (Asherman's syndrome). Synechia (or) may appear with complications during the postpartum or post-abortion period. With a broken cycle, such women should undergo a hysteroscopy as soon as possible to detect adhesions and remove them.
If there is a suspicion of the remains of a fetal egg or placenta, curettage with a hysteroscope is also prescribed. With the help of the procedure, it is possible to clarify the localization of the pathological zone and carry out its elimination without traumatizing the unchanged endometrium.
Preparation for the event
 Curettage is carried out on an emergency basis (for example, when bleeding is discovered) or planned. In the latter case, the intervention is performed a couple of days before the onset of menstruation.
Curettage is carried out on an emergency basis (for example, when bleeding is discovered) or planned. In the latter case, the intervention is performed a couple of days before the onset of menstruation.
This is necessary so that the procedure almost coincides with the period of physiological rejection of the functional layer of the endometrium (desquamation phase).
If a woman is to have a polyp excised under hysteroscopic supervision, the intervention is carried out immediately after menstruation. The mucosa in this phase of the cycle is thin, and the localization of the formation can be seen most accurately.
It is not recommended to carry out curettage in the middle of the cycle, as this threatens with prolonged bleeding after surgery. This reaction is explained by the fact that the functional layer of the endometrium increases in parallel with the growth of the follicle in the first half of the cycle.
As a result, it will be removed much earlier than the expected date of menstruation, which will lead to hormonal conflict. The physiological state will return to normal after the ovaries and uterus begin to work harmoniously with the central nervous system again.
Logically, curettage could be done during menstruation so that the natural rejection of the endometrium coincides with the surgical one. However, the diagnostic value of the procedure in this case is lost, since the detached layer has already undergone necrotic changes.
Diagnostic study
Separate diagnostic curettage with a hysteroscope is an in-depth examination method:

Contraindications for the procedure
Contraindications to curettage are:
- acute inflammatory;
- blood clotting disorders;
- suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the uterine wall;
- severe dysfunction of the heart and kidneys.
These contraindications can be ignored if there is a question of saving the patient's life (heavy bleeding, the threat of sepsis with the remains of the fetal egg, etc.). In this case, the tactics of the operation are discussed by the doctors collectively.
Analyzes required before scraping
 List of tests for planned curettage:
List of tests for planned curettage:
- complete blood count (CBC);
- general urinalysis (OAM);
- coagulogram;
- analysis for blood group and Rh factor;
- blood for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis;
- blood biochemistry (according to indications);
- , oncocytology.
From instrumental methods research is being carried out:
- electrocardiography;
- fluorography;
- hysteroscopy - performed before curettage to clarify the nature of the disease and localization of the formation, after - to control the thoroughness of tissue excision.
In case of emergency intervention, only the most necessary tests, with which you can assess the condition of the patient as a whole:
- blood type and Rh factor;
- coagulogram;
- blood for sugar.
A planned operation is performed on an empty stomach, you should first shave the hair in the perineum. You need to bring a bathrobe, shirt, socks, removable clean shoes, pads. A few days before the manipulation, douching, the use of vaginal tablets and suppositories should be stopped, and sexual intercourse should be abandoned.
Procedure steps
The procedure is performed under short-term mask or intravenous anesthesia. In some cases, paracervical anesthesia is used.
The operation consists of the following steps:

Technique
The operation is carried out according to the following technique:

The procedure is prescribed in all cases of suspected oncology. First, tissue is obtained from the cervical canal. The material is collected in a separate container. Next, they proceed to curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterus itself, the material is placed in the second container. In the direction of histology, it is necessary to indicate where exactly the tissue was taken from.
Traditional curettage
Traditionally, curettes are used for scraping. The forward movement of the instrument must be very careful to prevent perforation of the uterine wall. The reverse movement is carried out more vigorously, with a slight pressure on the wall. In this case, parts of the endometrium or the fetal egg are captured and excised.
 The sequence of curettage of the uterine cavity is as follows:
The sequence of curettage of the uterine cavity is as follows:
- front wall;
- back;
- side walls;
- corners of the uterus.
The size of the toolkit is gradually reduced. Manipulation is carried out until a feeling of smoothness of the uterine wall appears.
If the patient is shown a curettage with a hysteroscope, an optical instrument is inserted into the uterine cavity after the expansion of the cervical canal. The hysteroscope is a thin tube with a camera. The doctor carefully examines the uterine cavity, its walls.
After that, scraping of the mucosa is performed. If the patient has polyps, they are removed with a curette in parallel with curettage. At the end of the procedure, the hysteroscope is inserted again to evaluate the result. If not everything is removed, the curette is inserted again to achieve the proper result.
Not all neoplasms can be removed with curettage (some polyps, adhesions, myoma nodes). At the same time, special instruments are introduced into the uterine cavity through a hysteroscope, and the formation is removed under supervision.
Curettage with myoma
 The technique of curettage of the uterine cavity depends on the problem. An uneven, bumpy surface of the walls occurs with submucosal or interstitial myoma.
The technique of curettage of the uterine cavity depends on the problem. An uneven, bumpy surface of the walls occurs with submucosal or interstitial myoma.
Manipulation in this case is carried out very carefully so as not to violate the integrity of the capsule of the myoma node.
Damage to the latter can provoke bleeding, necrosis of the node and infection.
If uterine cancer is suspected
If a malignancy is suspected, the seized material can be very abundant. If the tumor has grown through all layers of the wall, the intervention can seriously injure the uterus.
Curettage for frozen pregnancy
 Removal and destruction of the fetal egg is performed after the expansion of the neck with the help of curettes and abortion collet. With a gestational age of less than 6-8 weeks, parts of the destroyed fetal egg are removed from the uterine cavity by means of an abortion collet.
Removal and destruction of the fetal egg is performed after the expansion of the neck with the help of curettes and abortion collet. With a gestational age of less than 6-8 weeks, parts of the destroyed fetal egg are removed from the uterine cavity by means of an abortion collet.
Scraping of the walls is carried out with a blunt curette No. 6, in the future, as the myometrium contracts and the uterus shrinks, sharper instruments of a smaller size are taken.
The curette is carefully advanced to the bottom of the uterus, movements are made towards the internal os: first, along the front, then along the back and side walls, the fetal egg is separated from the bed.
In parallel, the fallen off shell is separated and removed. With a sharp curette, the area of \u200b\u200bthe corners of the uterus is checked and the manipulation is completed.
The uterus during pregnancy cannot be scraped to the “crunch”, since such an intervention severely damages the muscular apparatus of the organ.
Postoperative period: how long to stay in the hospital?
After the procedure, an ice pack is placed on the abdomen so that the uterus contracts better and the bleeding stops. After some time, the woman is transferred to the ward, where she comes out of anesthesia.
They spend from several hours to several days in the ward, depending on the situation. With planned curettage, they are usually released home on the same day.
Normally, curettage passes without any pain, as anesthesia acts and takes about 20-30 minutes in general.
 After manipulation, the muscular layer of the uterus begins to contract intensively. The body thus stops uterine bleeding.
After manipulation, the muscular layer of the uterus begins to contract intensively. The body thus stops uterine bleeding.
The uterus fully recovers after curettage in about the same number of days as menstruation lasts. This process usually takes 3-5 days.
A few hours after the procedure, blood clots will be released from the vagina. At the same time, the woman experiences weakness, lethargy ( side effects anesthesia).
Along with bleeding, other symptoms may also occur.
Discharge after cleansing
In the first few hours, blood clots may be released. This is quite normal, since a wound surface has formed on the mucosa.
A few hours after the intervention, the intensity of bleeding decreases. For the next few days, the patient continues to be bothered by spotting yellow, pink or brownish discharge. The process of regeneration of the wound surface averages 3-6 days, but can last up to ten days.
The rapid cessation of discharge is not a favorable sign. This may indicate contraction of the cervix, low contractile activity of the myometrium, or accumulation of clots in the uterus.
Pain
 After coming out of anesthesia, many women experience menstrual pain. Unpleasant sensations can radiate to the lumbar region.
After coming out of anesthesia, many women experience menstrual pain. Unpleasant sensations can radiate to the lumbar region.
The pain syndrome lasts for several hours or days and usually does not require additional measures.
However, doctors usually advise women to take a pain reliever and an anti-inflammatory drug (such as ibuprofen) after surgery.
sexual relations
Women who have undergone curettage of the uterine cavity are shown sexual rest. Ideally, it should last one month or at least two weeks.
The need for abstinence is due to the fact that the neck remains open for some time, and there is a wound surface on the mucous membrane. These are suitable conditions for the attachment of an infection, which can lead to complications.
A negative point that may be associated with sex after scraping is the appearance of discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse. It is considered normal only if it lasts too long. If the pain persists for several months, you need to inform the gynecologist about it.
Pregnancy and childbirth after curettage of the uterine cavity
 The first menstruation after curettage may occur with some delay (in some cases up to four weeks or more), which is associated with hormonal failure. This is also considered normal after curettage.
The first menstruation after curettage may occur with some delay (in some cases up to four weeks or more), which is associated with hormonal failure. This is also considered normal after curettage.
The alarm should be sounded if menstruation does not occur for more than two months - this is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist.
In general, most women get their period after two to three weeks, which means that in a new cycle (i.e., with the onset of menstruation), there is theoretically a chance of getting pregnant.
Childbirth after the procedure, as a rule, proceeds well.
If a woman tries to conceive a child for six months or more after curettage, but there are no results, an additional examination by a gynecologist is necessary. Curettage should not adversely affect fertility, on the contrary, this procedure is often performed in complex treatment infertility.
The scheme of pregnancy planning after curettage is built depending on what caused the need for surgery. If a woman sets herself the goal of becoming pregnant after curettage, this must be reported to the gynecologist. The specialist will give an adequate assessment of the situation and recommend the timing of the start of pregnancy planning.
Possible complications after surgery
After scraping, the following complications may occur:

So, under what conditions should you immediately seek medical help:
- Bloody discharge after the operation stopped very quickly, while the stomach hurts a lot.
- The temperature rose to 38 o C and above.
- Severe pain syndrome, not relieved by analgesics, antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Abundant bleeding that does not stop for several hours (three or more pads are consumed in two hours).
- Profuse discharge with an unpleasant, putrid odor.
- General deterioration of health: severe weakness, dizziness, fainting.
The appearance of an acute (or exacerbation of a chronic gynecological disease) after curettage is also a reason for a visit to the doctor.
Treatment after the procedure
Therapeutic measures after the procedure:

The results of the histological test are usually obtained on the tenth day after brushing. It is important to come to the doctor at the specified time to discuss further treatment tactics.
Rehabilitation
For at least two weeks, you need to refrain from sexual activity (ideally - a month).
 What else can not be done:
What else can not be done:
- Use tampons (pads - you can).
- Douche.
- Go to the bath, sauna, sit in a hot bath (shower - you can and should).
- Engage in intense fitness, physical labor.
- Drink tablets containing acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) - contribute to bleeding.
Cleansing the uterus is a common and far from harmless procedure. If it is carried out by an experienced doctor, the risk of possible complications is low. Flow postoperative period depends on the woman herself. She should pay attention to the nature of the discharge, to distinguish the norm from the pathology.
Types, stages of scraping
Cleansing the uterus (lat. Abrasio cavi uteri) is a minor surgical intervention in gynecology, which can be performed mechanically or by vacuum. Procedures for the technique of carrying out almost does not differ from medical abortion and can be carried out for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
During mechanical cleaning of the uterus (or curettage), the gynecologist, using special equipment and tools, expands the cervix and penetrates into the uterine cavity through the cervical canal.
The hysteroscope is used during the surgical procedure. With its help, the doctor visually evaluates the cavity of the organ, determines the unaffected areas and performs a direct curettage: removes the upper layer of the mucous membrane. The doctor collects the extracted tissue samples in a test tube and sends it for histological examination.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterus is considered a more gentle intervention. It is carried out using a special tool - an aspiration syringe. The organ cavity, endometrium and neck are less traumatized, the woman tolerates the procedure well and the risk of complications is minimal.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterus is used for diagnostic purposes, for abortions, aspiration of missed pregnancy. The procedure is considered simple, effective and gentle.
Indications, contraindications

In gynecology, mechanical and vacuum curettage makes it possible to identify and treat most pathologies. Most often, cleaning the uterus is prescribed for endometriosis and bleeding. Conditions in which vacuum aspiration is used:
- Violation of the menstrual cycle with prolonged, massive bleeding.
- Scanty discharge from the genital tract.
- Post-abortion remains of the fetal egg.
- Postpartum placenta.
- Miscarriage.
- Frozen pregnancy with underdevelopment of the embryo.
- Abortion (up to 3 months).
Conditions in which uterine cleansing is prescribed mechanically (curettage):
- pathology of the endometrium.
- polyposis growths.
- Bleeding during menopause.
- Suspicion of a malignant neoplasm.
- Intrauterine adhesive process.
- Hyperplasia of the endometrium, endometriosis.
The procedure is contraindicated in women with ectopic pregnancy, neoplasms in the uterine cavity, malformations of the organ. Curettage is not prescribed with an active inflammatory process, severe somatic diseases.
If six months have not passed after the abortion and with massive bleeding, curettage is also not performed.
Period after scraping
After cleaning the uterus, spotting begins. How long they will last depends on how strong the body and its hormonal background.
Signs by which it can be argued that recovery after curettage is going well:
- Allocations last about a week, but not more than 10 days.
- Their volume gradually decreases and by the end acquires a smearing character.
- Soreness of moderate or slight intensity.
Brown discharge is a good and indicative sign. This suggests that the uterine cavity is being restored. But when they last more than 10 days, a visit to the gynecologist cannot be postponed.
If after the procedure a woman complains of severe pain and whiteness, it can be assumed that an inflammatory process begins with bleeding. This happens when an excessive amount of the germ layer is removed, and wounds have formed on the walls of the uterus.
If the discharge is profuse, accompanied by severe pain in the ovaries, fever and general weakness, the woman should be urgently hospitalized.
Complications

If curettage is carried out by an experienced and qualified specialist, then complications are quite rare, but possible. What pathology can develop after aspiration and curettage:
- Perforation of the uterus (puncture) as a result of mechanical curettage. Causes: technical difficulties in expanding the organ, excessive pressure, loose or altered uterine wall. Minor perforations heal spontaneously, and if larger injuries are surgically intervened and sutured.
- Rupture of the uterine wall. It can happen during the procedure when the clamps for fixing the cervix fly off. Minor injuries heal on their own, if extensive - suturing is performed.
- Violation of septic and antiseptic conditions, lack of supportive antibacterial treatment can lead to inflammation of the uterus.
- Adhesions with the formation of synechia - connective tissue growths that disrupt the menstrual and generative (formative) function of the ovaries.
- Profuse bleeding. The uterus has an intensive blood supply and the risk of this complication is quite high. The situation will worsen if a woman suffers from a clotting disorder. This is a dangerous condition that requires immediate hospitalization.
- Hematometra - accumulation of blood with a spasmodic cervix.
- Allergic reaction to drugs that were used for anesthesia.
If the procedure is carried out by a doctor with insufficient experience and technique, his strong and aggressive actions can lead to injury to the germ cells that cover the mucous membrane. With damage, new tissue growth becomes impossible. After scraping with endometriosis, with excessive cleaning of the mucosa, an incurable disease of adenomyosis often develops - a complete cessation of growth or active uncontrolled growth of the base layer of connective tissue.
Recovery period
Women who are shown cleaning the uterus should not be afraid of the procedure. If it is performed on modern equipment by a qualified doctor, everything will pass without harm to health.
Within two weeks after curettage, a woman should refrain from sexual intercourse and physical exertion, do not douche or take baths, do not overheat or overcool. And most importantly: with even minor signs of complications, you must definitely go to see a doctor.