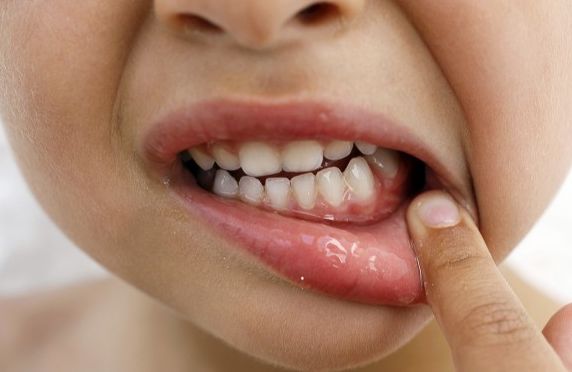
Inflammation of the gums in children a big problem for young parents. The gums become red and swollen for several reasons. The most common cause of inflammation in infants is teething. Children from the age of three are at risk of developing gingivitis.
You can help your child cope with the painful symptoms of teething at home with the help of topical preparations. If in doubt, it is better to ask the pediatrician for help. Gingivitis can be cured under the supervision of a pediatric dentist.
Inflammation of the gums with bleeding in gingivitis
Symptoms of gum disease
The first problems with teeth begin in a person in infancy, when these same teeth come out. Continue in preschool age when you want to put everything in your mouth, but you don’t like brushing your teeth at all. In schoolchildren, milk teeth change, which is also accompanied by trouble.
It is not difficult to notice inflammation of the gums in a child. The condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Redness. It can be localized in one place or spread over the entire surface.
- Puffiness. The inflamed gum area increases in size. In some forms of gingivitis, a growth may appear on the gum.
- Pain. When teething, the recurring pain causes the child to cry and act up. Inflammatory gum disease is most often characterized by aching pain.
- Itching, burning. There is a desire to scratch the sore spot.
- Increase in body temperature. The child's temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Bad breath. When teething appears rarely, it is a sign of infection. Pungent breath is characteristic of advanced gingivitis.
In infants, gum inflammation is more difficult to detect, because he still cannot complain of pain.

Inflammation of the gums - gingivitis
Parents often associate moodiness and temperature with a cold. Older children can talk about their condition.
You can examine the child's mouth at home. Wash your hands with soap before doing this. Then you can try to remove redness and swelling with the help of local remedies. The use of any drugs for an infant is best coordinated with a pediatrician.
Gums during teething
The timing of eruption of milk teeth in children is strictly individual. For some, the first tooth is at 3-4 months, for some, at a year old, the mouth is still empty. The process of teething in a child ends at 2 years.
The kid holds fists in his mouth, puts toys in, he saliva profusely. These are the first and main signs of teething. Caring parents during this period should slip a silicone teether to the baby.
The appearance of the first teeth is also accompanied by symptoms:
- Increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees.
- Loss of appetite.
- Irritability.
- Restless sleep.
Due to increased salivation, the baby may develop a cough, runny nose, irritation of the skin around the lips.
At the site of cutting baby tooth there is reddening of the gums. A bump is visible on the surface. If you touch it with your finger, you can feel the sharp edge of the tooth.
The lower incisors appear first, followed by the upper ones. In one-year-olds and children 2 years old, molars erupt. The appearance of molars is a longer and more painful process.
How to help your baby during teething
The appearance of teeth is a very difficult and hectic stage in the life of babies and their parents. The child experiences severe pain and discomfort. It is possible to alleviate the condition of the baby at home.
- Modern medicine offers many means and methods that will save the child from suffering during the appearance of teeth:
- gum massage. The method helps to relieve itching and pain speed up the process of teething. To massage the gums, you can use a simple gauze. It is moistened in water or chamomile broth, wrapped around a finger, and driven along the gum with light movements. For massage, special silicone fingertips are also used. They can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- The use of local anti-inflammatory drugs. Gels and ointments with herbal ingredients are widespread. For newborns, it is recommended to use "Baby Doctor, First Teeth". For children from 6 months old, you can use Kalgel with lidocaine, Cholisal and Dentinox.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs inside. You can bring down the child's temperature, relieve pain with the help of children's "Nurofen" in a convenient form of suspension. The drug can be used in children from three months.

Teething - inflammation
Some herbal preparations can cause allergies in a child. If a rash appears, swelling of the mucous membranes, you need to stop taking the remedy and consult a pediatrician.
During teething, special attention should be paid to the nutrition of the baby. Do not give sweetened drink to avoid the development of caries. You also need to take care of hygiene. The tongue of the baby should be cleaned in the morning with moistened gauze. All procedures should be carried out only with clean hands.

Teething aids
Inflammatory gum disease in children
The gums can become inflamed in newborns and adult children. The most common causes of gum disease are:
- improper oral hygiene;
- nutritional deficiencies (lack of vitamins and minerals);
- problems with nasal breathing;
- infectious diseases.
With insufficient oral hygiene, a favorable environment is created for the development of bacteria. During infectious diseases, pathogens enter the oral cavity from the respiratory system. When nasal breathing is disturbed, the child begins to breathe through the mouth. The mucous membranes dry out, the antibacterial function of saliva is disturbed. This leads to the active reproduction of microorganisms.

Causes of inflammation of the gums
Sometimes inflammation of the gums in young children is associated with eating soft foods. There is no chewing load on the gums. When the teeth appeared, it is necessary to give the child solid food - apple slices, pears, bread crusts.
Gingivitis in children
Children from 3 to 6 years old are a separate risk group for developing gingivitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the gums of moderate severity, in which the dental and periodontal tissues are not damaged. The development of gingivitis in babies is associated with improper hygiene and beriberi.
Gingivitis can be acute or chronic. Acute gingivitis is also called catarrhal. There are several forms of chronic gingivitis:
- marginal (simple);
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- desquamative;
- ulcerative.
AT childhood marginal gingivitis is the most common. A red growth on the gums in a child may indicate the development of hypertrophic gingivitis. Gingival tissues grow in the interdental space. Chronic gingivitis can be asymptomatic for years with periodic exacerbations.
What to do with gingivitis in a child, a pediatric dentist will tell you. Symptoms of inflammation can be removed independently.
Symptoms of acute gingivitis in a child
In acute gingivitis, the symptoms of inflammation are pronounced. The gum around the tooth turns red. Bleeding occurs when brushing teeth or chewing solid food. The child feels pain, is naughty, may refuse to eat. In rare cases, there is an increase in temperature.

Swollen gum near the tooth and hurts
How to treat acute gingivitis:
- Chamomile decoction. Older children can rinse their mouth. For babies, the gums are treated with moistened gauze.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments and gels. Helps get rid of red gums and relieve swelling.
- Antipyretics and painkillers. They are used only for severe inflammation.
During the treatment of gingivitis, it is imperative to exclude sweets from the child's diet.
It is necessary to clean the teeth and tongue from plaque twice a day. The procedure is carried out with cotton swabs.
When a child's gums become inflamed, you can give him a decoction of chamomile and sage to drink. All medications are used according to the instructions, taking into account contraindications.
Acute herpes stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. A disease occurs when pathogenic microorganisms enter the mouth. Herpes stomatitis often occurs in children at the age of 1 year when the herpes virus enters the body for the first time.
The disease can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. Stomatitis is accompanied by acute gingivitis. The main symptoms of the disease:
- An increase in body temperature up to 37-38 degrees with a mild course, up to 40 degrees with a severe course.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Anxiety.
- Reddened gums.
Stomatitis on the gum
Inflamed gums with herpetic stomatitis swell strongly and increase in size. The tissues can cover the dental crown up to the middle.
Treatment is carried out according to the prescription and under the supervision of a doctor. Antiviral, antihistamine, antipyretic drugs and vitamins are prescribed. To correct the functioning of the digestive system, sorbents and enzyme preparations are prescribed. The oral cavity must be treated with local anti-inflammatory and healing agents.
Prevention of gum disease in children
Inflammation of the gums is a very serious problem that can lead to serious damage to dental health. In young children, the disease is especially unpleasant.

Oral hygiene - prevention
Here are some basic preventive measures to help you avoid trouble:
- Hygiene oral cavity. Children can brush their teeth on their own under the supervision of their parents from the age of three.
- Proper nutrition. You need to provide a diet rich in vitamins and calcium.
- Purity. All vegetables, fruits must be washed and poured over with boiling water. Rattles, teethers, nipples should always be clean. You can communicate with the child only after washing your hands.
- Dentist. As soon as the child's teeth got out, it must be shown to the dentist.
- Red gums in a child should be the reason for going to the doctor.
- Inflammation of the gums is treated for a long time. Small children are not allowed to examine the mouth, lubricate the red gum, give them medicine to drink. Therefore, prevention is extremely important.
Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity in childhood can lead to dental problems in the future. Therefore, it is very important to start treatment on time. Be sure to seek help from a specialist before treating gum disease.
If your child less than a year, and you notice that he has a slight swelling in the gum area, you most likely should not worry - the child apparently has. In order not to be mistaken, pay attention to other signs of teething: baby began to cry more, does not sleep at night, is naughty, does not eat anything . Sometimes this process is also accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and skin rashes - something like an allergic reaction. All this is explained by the fact that all the forces of the child are directed to the process of teething. Immunity weakens, which leads to the activation of disease processes in the body.
But already when with swollen gums body temperature rises You need to call your local pediatrician. In addition to temperature, bleeding gums and non-healing scratches can also be a reason to call a doctor. This may be caused lack of vitamin C or cold. The doctor will prescribe everything you need.
In addition to the listed causes of gum swelling, the child may have other reasons - various inflammatory events. These include a flux (or fistula), a cyst (a growth in the form of a bump).
Other causes of gum swelling in children
Flux. Flux appears due to inflammation of the upper part of the tooth root - milk or permanent. As a result of inflammation, a swelling appears, or a fistula over the place where the inflammation manifested itself.
This inflammation is called Periodontitis and it appears as a result of untreated caries in time. If the situation has reached periodontitis, this can damage the germ of a new permanent tooth. That is why it is important to immediately treat the onset of caries.
But what to do with a child whose gums are swollen? First, see a doctor. Well, and secondly, before going to the doctor, you can do some activities. For example, use folk remedies treatment.
The most common and popular remedies are decoctions and infusions of various herbs and rinsing the mouth with them.
During teething, the child feels physiological discomfort, which causes a load on nervous system. Unlike older children, in babies of the first years of life, fatigue and exhaustion of nervous functions occur much faster. Inflammatory processes of the gums cause fever, cause diarrhea and prevent the child from falling asleep. Conventional drugs have only analgesic, or anti-inflammatory effect. Therefore, doctors usually recommend Dentokind, specially created for babies, which, in addition to analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, calms the nervous system and stabilizes sleep.
So, what herbs to take for? fit chamomile officinalis, sage leaves, oak bark, St. John's wort herb, yarrow herb.
The decoction is prepared as follows. Chop the herbs first. Two tablespoons of the collection (you can use all herbs at once, you can use one or those that are available) should be poured over 400 ml of boiling water. Then bring to a boil and simmer (simmer) for about five minutes over low heat. Cool, strain, squeeze. Give this decoction to the child to hold in his mouth (if he can, let him rinse) and spit it out. Rinse in this way five times a day. The broth should be warm.
If you don't have any herbs on hand, you can use baking soda. One teaspoon per glass hot water- Mix thoroughly and rinse in the same way.
Flux is a somewhat outdated name that is common only in everyday communication. AT modern dentistry such a pathology is called periostitis, which reflects the whole essence of the disease.
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, which covers the bone of the upper or lower jaw. As the pathological process develops, the lesion ceases to be local in nature and spreads to other tissues - an abscess appears on the gum surface.
In the photo: flux in a child of 7 years
Reasons for the appearance
The appearance of such a disease in childhood is most often associated with the penetration of an infection into the tissues, which provokes the development of a purulent process. There may be several reasons for this:
- Deep caries. It is known that milk teeth are less dense compared to permanent ones, therefore the occurrence of even a minor carious defect can cause a deep penetration of the infection in the shortest possible time.
- Little children have habit of tasting almost everything around them. This causes injury to the mucous membranes of the gums. And if pathogens get into such a wound, then due to the characteristics of the immune response of the child's body, the likelihood of periostitis is very high.
- Children aged 2-4 years are enough Difficulty maintaining good oral hygiene and brush your teeth properly. The accumulation of plaque and food particles in the gum pockets can cause their inflammation, followed by its spread deep into the tissues.
- Sometimes the flux appears after tooth extraction if there is a source of infection in the mouth: carious cavities, purulent gingivitis, tonsillitis. Pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate deep into the gums through an open wound and, against the background of reduced immunity, cause severe inflammation.
- Extremely rare, but periostitis can occur as a complication with purulent inflammation with a different localization, when the infection enters the periosteum with blood.
Main symptoms and manifestations
In the first days of the development of the inflammatory process, the child complains of moderate pain in the mouth. The gum at the site of inflammation slightly swells and becomes hyperemic. Children under the age of 3 may become moody, refuse to eat. Most often, this stage of the disease goes unnoticed, and parents attribute its first manifestations to the bad behavior of the baby.
As the purulent process develops, the child's condition becomes more severe. The pains acquire an intense pulsating character. A purulent focus is formed on the gum in the form of a small whitish formation on a red swollen background. Due to active inflammation, a significant swelling of the soft tissues of the face develops. If flux appears on upper jaw, then such edema can be located not only on the cheek, but also extends to the parotid region and the eye. If the localization of the flux is on the lower jaw, then the swelling of the tissues can also affect the cervical region.
The general condition of the baby suffers and the temperature rises (sometimes to fairly high numbers), the child complains of weakness, lack of appetite.
Possible Complications
Very often, parents underestimate the severity of such a disease in children as flux. However, this pathology is fraught with extremely serious complications that can even threaten the life of the baby.
- Abscess - the formation of a large purulent focus, the boundaries of which extend beyond the periosteum. Sometimes such abscesses can break out in the gums or even cheeks with the formation of fistulas, from which pus constantly flows.
- Phlegmon - the spread of purulent inflammation to neighboring anatomical regions. The most severe consequence of the flux, in which the risk of developing sepsis is very high - blood poisoning, often leading to death.
- The death of the rudiments of permanent teeth, leading to adentia. Severe inflammation within the gums can spread to the area of the permanent tooth germ and cause damage or death. As a result, when changing the milk dentition, molars will not erupt, which will require prosthetics already at a young age.
It is not difficult to suspect the development of complications. Usually, during treatment after opening the flux, the symptoms quickly begin to subside. After a few hours, the child's temperature decreases, swelling decreases, and the incision site practically does not hurt. But if the fever does not go away, and the pain syndrome only increases, then this is a reason for repeated emergency medical attention, because. inflammatory complications are likely to occur.
Treatment
Treatment of flux in children should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician. At the same time, the treatment tactics for a one-year-old infant and a child of 7 years old may differ due to the fact that before the natural change of the milk bite, it is possible temporary tooth extraction, which is highly undesirable until the age of 5-6 years.
In such cases, it is rarely possible to do without surgery. Quite often, one has to resort to a surgical method of treatment - opening the flux with the complete removal of all purulent masses and drainage of the resulting cavity. This allows you to both relieve acute pain and prevent the re-formation of the flux.
But surgical treatment is one of the stages of therapy. After visiting the dentist, the child's parents should continue treatment activities at home, which will include taking an antibiotic prescribed by a doctor, rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and applying remedies. traditional medicine.
 In the photo: treatment of flux in a child in the dentist's office
In the photo: treatment of flux in a child in the dentist's office
Treatment at home
In the first few days after visiting the dentist, when the pain syndrome can still disturb the baby, it is necessary to take anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, ibufen), which help both to remove the pain and contribute to the rapid subsidence of the inflammatory process.
An important point in home treatment is the use of antiseptic solutions for the treatment of the oral cavity. The dentist will tell you exactly how to rinse your child's mouth, but we will only give possible treatment options that can be used even in a small child.
- Aqueous solution of chlorhexidine. A ready-made pharmaceutical preparation is used, which is used to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day (after meals and before bedtime). It has a powerful antiseptic effect, but it does not irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Furacillin solution. You can cook it at home (1 tablet per 0.5 liters of water) or buy a ready-made product. Rinsing the mouth is carried out up to 5 times a day (it is advisable to do this after eating).
- Miramistin is detrimental to microorganisms and relieves inflammation well. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with 10 ml of solution 3-4 times a day. However, the drug should not be used before the age of three.
Rinsing the mouth with any of the listed means, the child should be carried out strictly under the supervision of adults in order to avoid accidents. The course of treatment should continue until the complete subsidence of all manifestations and healing of the purulent cavity.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes complement traditional treatment well. However, with such methods it is necessary to be careful in very young children, and for the treatment of babies under the age of 2 years, it is better not to use them at all.
- Soda solution. This remedy has a good anti-inflammatory effect. A teaspoon of dry powder of baking soda is dissolved in a large cup of warm boiled water and the child is allowed to rinse his mouth 3-4 times a day after eating. The effect of the treatment can be enhanced with iodine by adding a few drops of it to the rinse solution.
- Propolis tincture also perfectly relieves inflammation and has an antiseptic effect. To treat the oral cavity, 5 drops of tincture are dissolved in warm water of 200 ml and rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
- Decoctions of herbs. medicinal plants, such as chamomile, calendula, string are natural natural antiseptics and quickly relieve even severe inflammation. They allow both to cure the disease itself and to prevent the development of its complications. Decoctions are prepared daily, for which 2 tablespoons of a mixture of herbs are infused in half a liter of boiling water. Rinse the mouth with the decoction obtained 4-5 times a day until complete recovery.
homeopathic treatment
Homeopathic remedies can also be used in addition to the main treatment. You can not try to cure a child's flux only with homeopathy, since such remedies play only an auxiliary role. All appointments should be made only by a homeopathic doctor.
First aid for flux in a child
At the first symptoms of flux in a child, it is necessary to contact a pediatric dentist as soon as possible. However, if the road takes some time, you can provide first aid to the child yourself.
- Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibufen or paracetamol can help relieve acute pain, fever, and reduce inflammation.
- In order to relieve swelling, you can give the child an antihistamine at a dose appropriate for age (for example, suprastin, parlazin).
- A cold compress applied to the area of inflammation will relieve pain and swelling of the tissues.
- It is strictly forbidden to try to open the abscess yourself. This can provoke blood poisoning and further spread of the infection.
- If the dental flux burst on its own, in no case should you try to squeeze out its purulent contents. This can cause severe complications.
Prevention
Flux, like any other childhood disease, is easier to prevent than to treat later. The famous doctor Komarovsky prefers the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity from an early age:
- Regular visits to the dentist's office for routine examinations and sanitation of even the smallest carious cavities.
- Complete treatment of all foci of infection in the child's body.
- Parental control over the child's compliance with high-quality oral hygiene.
- Implementation of preventive appointments of the doctor after the extraction of teeth.
Only the observance of such simple rules can guarantee reliable protection both from dental flux, and from other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.