What mushrooms can be collected in a birch grove? Of course, boletus. The name speaks for itself. They love to grow under these native trees for us. It is worth noting that the name is prefabricated, it denotes more than one variety of mushrooms. All of them belong to a single genus - Obabkovye. The mushrooms included in this group have one main difference that unites them. This is the color of the hat, which has brown shades.
Description
In total, there are almost 40 varieties of this mushroom. But not all of them grow with us. The most common in our country can be considered such types of boletus: ordinary, harsh, pinking, gray, multi-colored. Each of these mushrooms feels great next to birches, with which they form mycorrhiza. But there are boletus under other trees - aspen, poplar. Most often, such mushrooms grow in places that are well warmed up by the sun, but the soil does not dry out much.
Let us consider in more detail the main varieties of boletus boletus:
Ordinary

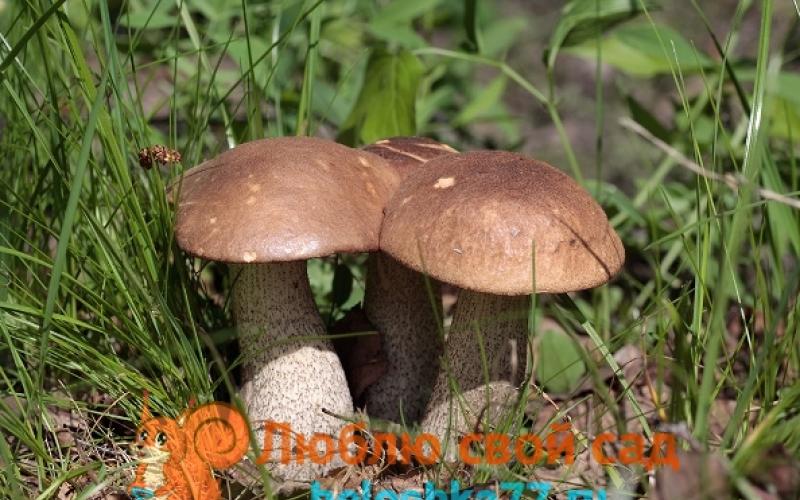
His hat has a brown color with a reddish tint. Its surface is slightly mucous, in dry weather it begins to gleam. In an adult mushroom, the hat resembles a pillow, in a young one it is a convex hemisphere. The diameter can reach 15 cm. The leg sometimes grows up to 17 cm in height, reaches 4 cm in width. It expands slightly towards the bottom, and the color can be white-cream and becomes grayish, ocher over time. On the cut, the white flesh of the boletus may acquire a pinkish tint.
Grey

This mushroom has another name - hornbeam. It has similar characteristics, but its hat is darker, has a shade of brown-olive, grayish. Its surface has bumps, wrinkles, and it tends to crack when it gets dry. The leg, in comparison with the common boletus, is lower. Brownish scales are observed on its light surface. When cut, the flesh turns purple, and eventually black.
Harsh

He likes to grow on sands, loams, especially if there are poplars and aspens nearby. The cap has pubescence hanging over the tubules. When the mushroom is young, it practically does not separate from the stem. The surface of the cap is brown. The pulp is also dark, the older the mushroom, the darker it is. The leg has scales, its shape is club-shaped. On the cut, the flesh becomes pinkish, and at the bottom of the leg - lilac.
When to Collect

Boletus mushrooms are sometimes also called "spikelets" or "haymakers". And all because these mushrooms appear at the time when they begin to mow hay, and rye is already earing in the fields. At this time, raspberries and mountain ash begin to bloom, viburnum hides in white. This is June. Further, you can collect boletus boletus throughout the summer and in the autumn.
Where does it grow
The very first mushrooms should be looked for in open areas. Edges, clearings, which are well heated by the sun - these are the places to look for boletus. As for the trees, everything is clear by the name of the mushroom. They can grow in dense forests, often mixed. Also, small groves have chosen boletus, you can find them under single trees.
This mushroom feels great in different climatic conditions. They are collected even in the tundra, of course, near the birches. Even if they are short, low, which is typical for the Arctic forests. The main condition is the root system of birch. After all, it is she who provides food to the mushrooms.
False boletus - description

Like most edible mushrooms, the boletus has its counterparts, the use of which is not recommended or strictly prohibited. The twin of this fungus is the false boletus. It is called gall fungus. It should be said right away that it is quite difficult to distinguish it from a real tasty mushroom. But probably.
In the gall fungus, the cap has similar shades, the leg is also covered with scales. The first difference that helps to find out that the gall fungus came to you is the taste of cooked prey. The fact is that the false boletus is extremely bitter, as evidenced by its second name. If even a small slice gets into a pot or pan, the whole portion will be spoiled.
External signs can also tell you that you have found a false boletus. Firstly, in a real mushroom, the pattern on the leg resembles a birch. The false scales are arranged in a different way. Secondly, the gall fungus has streaks on its stem that resemble human blood vessels.
The hat is also different. This boletus has more inconspicuous shades. And the false one has a hat with a brick, greenish color or bright brown. If you notice greenish tints on the boletus, then you should not take it, most likely it is a poisonous mushroom. It is necessary to consider it from below. Under the cap, the edible boletus has a light, whitish color. The false mushroom has a pinkish tint. In addition, it is characterized by a velvety cap surface and pink flesh at the break.
It is very important to be able to distinguish a real mushroom from a false double, your health depends on it.
Compound
The boletus contains many useful components. Firstly, it has a balanced protein containing leucine, tyrosine, glutamine, arginine. As for vitamins, they are also present in this mushroom. Namely, vitamins PP, B, D, E. The following components of the boletus can be distinguished:
- Phosphoric acid;
- Carotene;
- Iron;
- Calcium;
- Sodium;
- Potassium.
Beneficial features

One of the positive properties of this mushroom is the ability to remove toxins. This is due to the dietary fiber contained in the boletus. They perfectly absorb all the negative, and then removed naturally. Boletus boletus can be used as an aid in the treatment of:
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Violations of the amount of sugar in the blood;
- Kidney pathologies;
- skin problems;
- Diseases of the mucous membranes.
It is worth noting that the mushroom is useful for the musculoskeletal system. The phosphoric acid contained in it is actively involved in the process of building enzymes. So this product, as we see, is quite valuable in many cases.
How to cook
First of all, you need to know that boletus can be cooked without cooking. However, purchased mushrooms and those that are collected in places near the roads still need to be boiled. How long to cook, the question is also controversial. Some only bring to a boil, others cook for 20-30 minutes. Experts recommend boiling on average up to 40 minutes. This, of course, will save the mushrooms from many taste qualities and useful trace elements. But it will keep you safe.

First of all, you need to clean each mushroom. The dark place at the root is cut off during this process, the caps are cut to check if there are insects, worms.
If the mushrooms are still young, then they can be fried immediately, do not cook before that. In this case, they will be more solid. This cooking method is great, for example, for cooking fried boletus with potatoes. Mushrooms remain crispy and potatoes become soft. If the mushrooms are pre-boiled, they will be softer.
If you do not want to cook them, then you can hold the boletus for up to 20 minutes in salted water. This will help decontaminate your prey. Roasting time - no more than 15 minutes.
A very tasty dish - fried boletus with sour cream. Mushrooms need to be cleaned, washed, finely chopped. For 20 minutes they are fried in a pan with heated sunflower oil. As a result, a golden crust should form. Then chopped onion rings are added, everything is cooked together for another 5 minutes. From spices, you only need to add salt and pepper. At the end of frying, sour cream is added to the pan, lightly whipped with flour. All this is stewed for 10 minutes, you need to mix constantly. That's all - delicious boletus is ready!

To cook mushroom soup, you need to take 5-6 large boletus mushrooms, about a 4-liter pan. Mushrooms need to be cleaned, washed, finely chopped. To know what pieces you will get in the soup, divide them by about 2. That is, if you like about 1 cm slices in the soup, then cut 2 cm. They will double down.
Next, over medium heat, the mushrooms are boiled in salted water. Remove the foam after boiling, reduce the heat and cook the mushrooms for about 20 minutes. While this process lasts, you can prepare the vegetables. We clean the average carrot, wash it, three on a grater. 3 large potatoes are also washed and peeled, cut into strips. Peel the large onion, wash and cut into small pieces.
When the mushrooms have boiled for a sufficient time, you need to check the broth for salt. If necessary, add it, and then you can add vegetables. First, we throw onions into the pan, after 5 minutes it's time to add carrots, after the same amount - potatoes. The foam that forms on the surface of the broth must be constantly removed. At the end, you can add black pepper to taste.
Serve this soup with sour cream and fresh chopped dill. Before that, 1 clove of garlic is squeezed or finely chopped into each plate. Bon appetit!

Pickling is one of the favorite ways to harvest mushrooms for the winter, including boletus. To make them tastier, you can use this recipe.
First, the mushrooms are cleaned and washed. Young ones can be left whole or cut into 2-3 pieces. Old mushrooms are cut into smaller pieces. It is important to consider that they will boil down a lot. When cooking, it is necessary to constantly remove the foam, it is especially strongly formed during boiling.
You can cook until the moment when the mushrooms sink to the bottom of the pan. Then they are filtered, washed and poured with fresh water. Now you need to boil for another 10 minutes. Then you can add spices. 125 ml of vinegar is poured into the broth, 40 g of sugar and the same amount of salt are poured. All this for 1 liter of water. With these spices, mushrooms are cooked for another 25 minutes. Then you can add the rest of the ingredients - allspice (10 pcs.), Bay leaf (2 pcs.), Cloves (3 pcs.).
Ready mushrooms are laid out in jars, poured with marinade in which they were cooked. Boletus mushrooms are rolled up with tin lids, after which they are covered with a blanket or jacket until they have cooled completely. Only then they need to be removed to a cool room - a cellar, for example.

The key to a good freezing of mushrooms is their proper preparation. Boletus must be well sorted out, discarding those affected by rot or worms. Then the mushrooms are cleaned of debris. Now you can wash them. For this, warm water is used. Rinse at least 3 times. Then it is very important to dry the mushrooms well. To do this, they need to be spread out in a thin layer on an absorbent surface - a paper napkin or cotton cloth.
Now you can start freezing. So, you can freeze raw mushrooms. You need to choose the youngest, fleshy boletus. It is best to lay them out on a flat surface and send them to the freezer. Now you have to wait a while until each mushroom becomes hard as ice. Only after that you can pour them into a bag or a plastic container. If you freeze everything at once, putting it in a bag, then the mushrooms will stick together, turn into a whole lump. And with a separate freeze, you can pour yourself mushrooms as much as you need, and send the rest back to the freezer. Do not forget, you can not re-freeze mushrooms!
You can also freeze boiled mushrooms. To do this, peeled and chopped boletus is boiled for up to 40 minutes, it is possible in several waters, washing the mushrooms in between. Then we drain the water with a colander, dry it in it. Now the mushrooms can be laid out in containers or bags. But keep the portions, again, so that you do not have to re-freeze extra boletus.
Some housewives also freeze fried mushrooms. To do this, you just need to fry the boletus in sunflower oil to the extent you like.
Quiet hunting. On mushrooms with an action camera. White, boletus, boletus: video
Boletus mushrooms are tasty, and even healthy. Enjoy them, but be careful not to be fooled by false birch boletus!
Boletus mushrooms are popularly known as birch mushrooms and blackheads, this type of spongy cap mushrooms belongs to the genus Leccinum, or Leccinum (Leccinum) of the Boletaceae family.
The name of this fungus is “speaking”, and indicates that it forms mycorrhiza with birches, next to which it grows.
Characteristics of the boletus mushroom
Hat

The hat of the boletus is 4-12 cm in diameter, gray, brown or brownish, sometimes almost black. Its shape is like a swollen pillow.
pulp

The pulp is colored uniformly, in light colors, does not change color when broken.
Leg

The leg is 1.5-4 cm in diameter, white or grayish in color, scaly, tapering upwards.

Boletus boletus are widespread in the countries of Eurasia, as well as in North and South America. They are inhabitants of deciduous forests, growing in birch groves.

The picking season for boletus begins at the end of June and continues until the beginning of November.

All boletus mushrooms are edible mushrooms, some species differ slightly in nutritional qualities. These mushrooms contain vitamins such as vitamin B1, B2, PP and vitamin C.
In cooking, boletus mushrooms are used in fried, boiled and pickled form, they are also harvested for future use by drying. When dried, the mushroom turns black.
Boletus mushrooms are used as a filling for pizza, pie, roll, as a base for sauces and in powder form. These mushrooms go well with potatoes, buckwheat, lentils, carrots, cabbage, peppers.
Boletus mushrooms are forbidden to be eaten by people with ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract, with individual intolerance and children.
Types of boletus mushroom

The hat is from white to dark gray and black, in a young mushroom it is white below, in a mature mushroom it is grayish-brown. Leg thickened at the bottom, white, covered with scales. The pulp is white, does not change color when broken.
It grows in birch groves from the first half of summer to autumn, as well as in the tundra and forest-tundra. Found in Eurasia, North and South America.
An edible mushroom, it is used in food in fried, boiled, dried and pickled forms.

The hat is 7-14 cm in diameter, at first hemispherical in shape, with an edge curved at the bottom, later cushion-shaped. The surface is uneven, wrinkled, velvety. The skin is dry, matte, in wet weather it becomes shiny, olive-brown. The flesh is white, soft in the cap, fibrous in the stalk, becoming pinkish-violet in the cut and gradually almost black. Leg 5-13 cm long, about 4 cm in diameter, cylindrical in shape, with a club-shaped thickening at the bottom. The color of the stem is olive-gray above, brownish below, the surface is scaly.
Mycorrhiza forms with hornbeam, hazel, poplar. It grows in deciduous forests of Eurasia. The season is June-October.
Edible mushroom, poorly stored.

The cap is 6-15 cm in diameter, in young mushrooms it is hemispherical in shape, with age it becomes convex, cushion-shaped, the center is depressed. The skin is slightly pubescent or scaly, in mature mushrooms it is naked, smooth, matte, becomes slimy in wet weather. The color of the cap is grey-brown to reddish-brown, darkening with age. The flesh is firm, white, yellowish-green at the base of the stem, turning pink or red when broken. It has a pleasant taste and a slight mushroom smell. Leg 5-16 cm in height, 1-3.5 cm in thickness, cylindrical or spindle-shaped, pointed at the base, solid, whitish or cream above, brownish, scaly below.
Occurs from late July to mid-November in deciduous and mixed forests, mycorrhizal former with aspen and poplars. Rare view.
Edible mushroom with firm flesh. Used for fresh and dried food.

The hat is about 16 cm in diameter, convex or cushion-shaped. Light, whitish or pale brown, dry surface. The pulp is white, soft, greenish, watery. Does not change color on the cut, taste and smell are not expressed. The leg is long, thin, white or grayish in color.
Mycorrhiza forms with birch, grows near swamps, in damp birch and mixed forests. The fruiting season starts in July and lasts until the end of September.
An edible mushroom, with loose, strongly boiled pulp, young mushrooms are eaten.

Hat 5-9 cm in diameter, dark brown or black. The leg is scaly.
It grows in pine and birch forests, in damp places, in swamps. Distributed in Eurasia, from Western Europe to Eastern Siberia. The collection season is July-September.

The cap is convex, later becomes cushion-shaped, about 15 cm in diameter. The skin is dry, from gray-brown to black, decorated with a light marble pattern. The pulp is white, dense, turns pink on the cut. The stalk is long, thin, thickens towards the base, sometimes curved.
It grows in damp birch forests, in separate groups, in Eurasia and North America. Fruits in June-October.
Edible mushroom, used fresh for food, suitable for drying and pickling.

The cap is hemispherical in young mushrooms, later becomes cushion-shaped, 5-15 cm in diameter. The skin is dry, smooth, sometimes felty, cracking, yellow-brown. The pulp is light yellow in color, soft, on the cut it first turns red or brown, then blackens. Leg 5-12 cm high, 1-3 cm thick, cylindrical or club-shaped thickened downwards, yellowish, scaly.
Grows next to beeches and oaks in warm regions of Europe, singly or in groups. The harvest season runs from June to September.
Edible mushroom, used fresh, dried, pickled. Blackens during drying.

The cap is convex or pillow-shaped. The skin is light brown, darkens with age, the surface is smooth. The pulp is white, turns pink on the cut. The leg is long, thin, light with dark scales.
Occurs in autumn in birch groves of Eurasia.
Edible mushroom.

Outwardly, it resembles a common boletus. The hat of this species is motley, dirty brown. The pulp is white, turns pink on the cut. The leg is white with a light blue tint, scaly.
Edible mushroom.
Poisonous and inedible species of boletus mushroom

The cap diameter is 4-10 cm, the shape is hemispherical, later round-cushion-shaped or prostrate, the surface is dry, pubescent or velvety, later smooth, from yellow-brown to gray or brown. The pulp is white, reddens when cut. The smell is not expressed, the taste is bitter. Leg 3-12.5 cm in height, 1.5-3 cm in thickness, cylindrical or club-shaped, expanding downwards, fibrous, cream-ocher, yellowish, reticulate.
The cosmopolitan mushroom grows in coniferous and deciduous forests on all continents, both singly and in groups. The fruiting season is June-October.
Young gall fungus is confused with white fungus and boletus. It differs from the latter in the absence of scales on the leg.
Inedible mushroom.

Boletus spores are poorly separated from the pulp. Therefore, a solution is prepared from one part of the pulp and 100 parts of water, which is poured over the opened birch roots. After that, the roots are additionally moisturized.
In the dry season, the soil is regularly sprayed with a spray bottle. Watering is carried out in the afternoon, when the sun's rays do not fall on the boletus. Humidification is also necessary immediately after the first fruiting bodies appear. Water the bed with plain water daily. The first crop is harvested one year after sowing.
Calorie boletus mushroom
100 g of fresh mushroom contains 31 kcal. The energy value:
- Proteins, g:…………………2.3
- Fats, g……………………..0.9
- Carbohydrates, g……………….3.7

- In folk medicine, boletus is used to treat diseases of the nervous system, kidney disease, as well as to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Fresh boletus is recommended for inclusion in the diet of those who lose weight, as mushrooms are a low-calorie product.
Kira Stoletova
The boletus mushroom is one of the most delicious and healthy basidiomycetes. With its qualitative characteristics, it is equated to the kings of the forest - porcini mushrooms. Belongs to the Boletov family, the genus Obabok. In our forests, the boletus mushroom is represented by several species. All of them are edible, but differ in taste.

general characteristics
The cap of the mushroom is matte, has a hemispherical shape, painted in a grayish or pale chocolate color. As they grow older, it begins to resemble a pillow. Its diameter can reach 18 cm. With an increase in humidity, sticky mucus appears on the surface of the cap.
The boletus looks like a boletus. The main differences are the shape of the legs, the color scheme of the hat. The long dense and fibrous leg, expanding in the lower part, reaches 9-12 cm in height. The color of the legs is off-white. In the lower part, its surface is covered with small dark scales.
The hymenophore is tubular. It is painted white, as it grows older it becomes gray, watery-loose. The flesh is white and has a greenish tinge. On the cut, when exposed to air, it becomes slightly gray. Exudes a pleasant mushroom aroma.
In young specimens, the fruiting body is dense and delicate in taste, in old specimens it is loose, contains a large amount of moisture. The boletus grows singly or in groups. The harvest season starts in May-June, depending on the region, and ends in late autumn. Spring boletus appears very first.
Kinds
There are more than 40 types of boletus. The most popular with mushroom pickers:
- common boletus;
- boletus marsh or white;
- boletus pinkish or oxidizing;
- boletus gray or hornbeam;
- black boletus, which is popularly called blackhead;
- boletus multicolored.
On the territory of Russia, the most famous are the common boletus and the hornbeam. In addition to them, there are 7 more varieties. All types of boletus are edible mushrooms.
False boletus, dangerous to human health, is distinguished by the pink color of the hymenophore in old representatives. In a young false boletus, the hymenophore is white. Young specimens are recognized by pressing on the spore-bearing layer: if it turns pink, then the fungus is poisonous.
Obabok birch
Common boletus is an edible mushroom that grows in birch plantations, deciduous, mixed forests. His hat is domed, diameter - 15 cm. The boletus has a hat color from dark chocolate to grayish, which depends on the region in which he lives. The surface of the cap is thin felt or bare.
The hymenophore is tubular, easily separated from the lower part of the cap. The young hymenophore is white, becoming grayish as it matures. Spores are olive-brown. The fruit body is white, does not change color at all or acquires a slightly pink tint when cut.
Bolotnik
Marsh boletus or white birch, growing in small groups or singly in humid areas, located on the outskirts of swamps and lakes. Appears in September after heavy rain. Fruits until the end of autumn. Forms mycorrhiza with birch root system.

The cap of the swamp in diameter reaches 12 cm. The shape is convex, then pillow-shaped. The surface is dry, white or off-white. The old bog is painted greenish-gray. Such specimens are no longer collected.
In young mushrooms, the hymenophore is tubular, gray-green. The pulp is watery, white, loose structure, does not change color on the cut. Exudes a mushroom aroma. The leg is high, thin, slightly expanded at the bottom. Painted white, covered with small scales.
Boletus pinkish (oxidizing)
Pinking boletus (edible mushroom) forms mycorrhiza with tree and shrub birches. Gather p. turning pink in the northern forests, where he prefers to grow on the slopes of groves, in the highlands, on waterlogged soils. Appears in the forests in autumn after heavy rains. It has a small hat, painted in yellow-brown color. The tubular hymenophore is white and later becomes gray.
The white stem is shorter when compared to other mushrooms in this genus. Its surface is covered with a large number of gray scales. In some instances, the legs are bent to the side, from where more light falls. The pulp is white, dense, reddens on the cut.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
This type of boletus is characterized by a peculiar “marble” color of the cap: brown areas are interspersed with lighter and even almost white in color. It is she who distinguishes the item turning pink from the ordinary in appearance. These mushrooms are also known in the northern part of Western Europe.
Grabovik
The gray boletus is popularly called the hornbeam. A young specimen growing in the same area where the item is oxidized is distinguished by a wrinkled structure of a hemispherical cap, its diameter is 6-15 cm. Its color palette is diverse. The surface of the hat can be painted in the following colors:
- grey;
- yellow;
- black;
- olive brown.
The stalk, 6-18 cm high, is initially strongly swollen, later becomes cylindrical, narrowed downwards. When pressed, it takes on a darker tone. Gray boletus mushrooms form mycorrhiza (fungal root) with birches, oaks, beeches and nuts. The collection begins in the month of June, when the mountain ash blossoms.
blackhead
These mushrooms, growing in wet and swampy soils, are called "black" for the dark color of the cap. Worms of this species are very rare, which distinguishes them from other representatives of the genus.
The first mushrooms appear in the summer. The peak of fruiting is observed in September. If the summer was dry, they will not appear.
Description of black boletus mushroom:
- hat 16 cm in diameter, matte black or chocolate brown;
- the surface of the fruiting body is dry, velvety to the touch, after rain and with increasing humidity - sticky, slimy;
- the pulp has a hardish structure, the pores of the hymenophore turn blue on the cut;
- the leg is off-white, thickened, about 12 cm high.
Obabok color (multi-colored)

The main symbiont for the formation of mycorrhiza is birch, the secondary one is beech, aspen. Boletus Multicolored is painted in gray-white color, with pronounced strokes on the surface of the cap. In diameter, it reaches 12 cm.
The flesh is white, on the cut after a while it turns pink. The smell is barely perceptible. The tubular hymenophore is finely porous. Spores are light brown.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
If we compare the common boletus and the multi-colored boletus, then the second one has a more compact size, which is expressed in a smaller diameter of the cap, height and thickness of the stem. As the fungus matures, the cap changes from closed to slightly convex. The taste of the pulp is pleasant, although weak. The tubules of the hymenophore are finely porous, light gray in young specimens, light brown in adults, and dark spots may appear on them. When pressed, the tubes change color - turn pink. The length of the stem of a multi-colored item depends on the height of the moss in which they grow.
Fruiting from June to October, they are found mainly in swamps and mossy forest areas.
Beneficial features
High nutritional value and low calorie content make these mushrooms indispensable ingredients in the diet of people who want to lose weight or gain muscle mass. The fibrous pulp after heat treatment resembles the taste of meat. The chemical composition of the boletus includes a protein that includes 8 essential amino acids that the human body is not able to synthesize on its own.
The pulp of the mushroom includes 35% protein, about 14% glucose, 4% fat, 25% fiber. Among the useful properties of the fungus, the presence in the composition of a large number of trace elements and vitamins is noted:
- thiamine;
- zinc;
- nicotinic acid (vitamin PP, vitamin B5, niacin);
- vitamins of group B, C, D, E, A;
- magnesium;
- sodium;
- phosphorus;
- iron;
- manganese.
This species holds the record for manganese content. Phosphoric (orthophosphoric) acid, present in the composition, has a positive effect on the functioning of the musculoskeletal system due to participation in the construction of enzymatic cells. White mushroom (boletus) and boletus are considered competitive specimens. They have been actively used in folk and traditional medicine for a long time.
Contraindications
As such, there are no contraindications to the use of birch, but it is prohibited for individual intolerance. It is undesirable to prepare such food for children under 8 years of age and people suffering from stomach ulcers. The fiber contained in mushrooms is digested for too long, which can cause the stomach to “stop” in babies.
You should not collect boletus in forests located near factories, landfills, in public places and near highways. They accumulate toxins in themselves. An overripe mushroom is also dangerous.
Application

The boletus is ranked among the delicacy types of mushrooms, so most people only know about its use in cooking. In fact, this representative of basidiomycetes can be a good substitute for drugs. The content of fiber and protein makes it possible to prepare dietary supplements for athletes on its basis.
The boletus will be useful in agriculture. After burning mushroom bodies, ash is formed, which contains calcium, phosphorus, zinc and nitrogen, which ensures stable nutrition and does not allow the soil to lose its quality. Mushroom products are suitable for compound feed for cattle, pigs and poultry.
In cooking
The product must be processed before use. First, it should be cleaned of adhering dirt, remove the skin, cut off the lower part of the leg. If the product needs to be dried, it should not be washed. Dirt is cleaned, and then the hat is simply wiped with a damp cloth.
So that the product prepared for gourmet dishes does not turn blue, after cleaning it is soaked in water with a small amount of lemon juice (juice from 0.5 fruit per 1 liter of water). It does not need to be soaked for several hours like milk mushrooms, 20-30 minutes is enough. Cooking technology involves double boiling. For the first time, it takes only 5 minutes to boil the product after boiling water. Then it is transferred to another pan, put a bay leaf, a whole onion, a couple of peas of allspice, cook for 20-30 minutes until fully cooked.
Boiled raw materials are used for marinating, cooking soups, mushroom caviar, salads and other dishes. For the winter, you can prepare dried mushrooms or freeze fresh or boiled products in portions. Storage requires compliance with the rules:
- dried fruits with signs of mold must be disposed of;
- frozen products are used immediately and are not re-frozen;
- when the brine becomes cloudy in the jar, the product is disposed of.
In medicine
In folk medicine, it is used in tinctures and ointments to eliminate pain in osteochondrosis or gout. Affected areas should be treated 3-4 times a day. Tinctures are taken 2-3 times a day to increase immunity and sexual activity. Separate components of basidiomycete in combination with alcohol give an analgesic effect, eliminate nervousness (i.e., they have some sedative effect).
The exceptional properties of this fungus make it possible to use it in the manufacture of drugs for weight loss. In cosmetology, an extract from it is used as a rejuvenating component.
cultivation
The cultivation of basidiomycetes is actively carried out. At home, it is easy to grow a clearing with delicacy mushrooms on a personal plot. You can plant spores collected on your own in the country or buy ready-made mycelium. Basidiomycete will bear fruit well in the area where there are birch trees from 2 to 4 years old.
If you want to collect spores with your own hands, pick up several old fruiting bodies. At a distance of 50 cm from the trunk, beds are made with a depth of 21-31 cm. Crushed stone is laid at the bottom, then coarse-grained sand and a turf mixture. All this must be covered with a layer of high-quality compost.
If the hymenophore collected from mushrooms is solid, it is better to soak it together with gelatin and dolomite flour in a ratio of 1: 0.2: 0.3. The mixture is placed in the holes, covered with compost, they should be mulched with a turf mixture on top. Stably high soil moisture is maintained within 70%. To successfully grow a product on the site, special attention should be paid to harvesting. The main thing is to make sure that the mycelium that produces shoots is not destroyed, otherwise it will be the last harvest.
An easier option is to buy a beginner's kit, which includes a special basket with "seed" material, substrate and detailed instructions. You can easily find them in any specialized store.
Acquaintance with boletus mushrooms Signs of difference
Silent hunting Mushroom picking Boletus honey agaric
False and real boletus
Conclusion
Boletus is a delicacy edible type of mushroom, including more than 40 subspecies. The name is due to the occurrence of symbiosis with birch. All representatives are rich in nutrients and minerals. Today, the planting of forest basidiomycetes in summer cottages is actively practiced.
Systematics:- Division: Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes)
- Subdivision: Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes)
- Class: Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes)
- Subclass: Agaricomycetidae (Agaricomycetes)
- Order: Boletales (Boletales)
- Family: Boletaceae (Boletaceae)
- Genus: Leccinum (Obabok)
- View: Leccinum scabrum (boletus)
- Other names for mushroom:
Synonyms:
Common boletus
birch
Obabok
Obabok birch
Hat:
In boletus, the hat can vary from light gray to dark brown (the color obviously depends on the growing conditions and the type of tree with which mycorrhiza is formed). The shape is semi-spherical, then pillow-shaped, naked or thin-felt, up to 15 cm in diameter, slightly slimy in wet weather. The flesh is white, not changing color or slightly turning pink, with a pleasant "mushroom" smell and taste. In old mushrooms, the flesh becomes very spongy, watery.
Spore layer:
White, then dirty gray, the tubes are long, often eaten by someone, easily separated from the cap.
Spore powder:
Olive brown.
Leg:
The length of the boletus leg can reach 15 cm, diameter up to 3 cm, solid. The shape of the leg is cylindrical, somewhat expanded below, gray-whitish, covered with dark longitudinal scales. The pulp of the leg becomes wood-fibrous, hard with age.
Spreading:
The boletus (Leccinum scabrum) grows from early summer to late autumn in deciduous (preferably birch) and mixed forests, in some years very abundantly. It is sometimes found in surprising quantities in spruce plantations interspersed with birch. It also gives good yields in very young birch forests, appearing there almost first among commercial mushrooms.
Similar species:
The genus Boletus has many species and subspecies, many of them are very similar to each other. The main difference between "" (a group of species united under this name) and "" (another group of species) is that they turn blue at a break, and boletus does not. Thus, it is easy to distinguish between them, although the meaning of such an arbitrary classification is not entirely clear to me. Moreover, in fact, there are enough among the "boletus" and species that change color - for example,. In general, the further into the forest, the more varieties of bolets.
It is more useful to distinguish Boletus (and all decent mushrooms) from. The latter, in addition to the disgusting taste, is distinguished by the pinkish color of the tubes, the special “greasy” texture of the pulp, a peculiar mesh pattern on the stem (the pattern is like that of a porcini mushroom, only dark), a tuberous stem, and unusual places of growth (around stumps, near ditches, in dark coniferous forests, etc.). In practice, confusing these mushrooms is not dangerous, but insulting.
Edibility:
boletus - normal edible mushroom
. Some (Western) sources indicate that only the caps are edible, and the legs are supposedly too hard. Absurd! Cooked hats are distinguished by a sickly gelatinous texture, while the legs always remain strong and collected. The only thing that all reasonable people agree on is that in older fungi the tubular layer must be removed. (And, ideally, take it back to the forest.)

Author's notes:
Despite the seeming routine, the boletus is a rather mysterious mushroom. First, fruitfulness. For several years, it can grow in homeric quantities anywhere and everywhere. In the early 90s, in the Naro-Fominsk region, the boletus was, without exaggeration, the most common mushroom. He was loaded with buckets, troughs, trunks. And in one year he disappeared, and he is not there until now. as it was enough, it is (despite the crowds of greedy summer residents), and the boletus has disappeared. From time to time only monstrous freaks come across: small, thin, twisted.
In the summer of 2002, for obvious reasons, there were no mushroom pickers at all, and what do you think? occasionally came across quite decent boletus. Something will happen next time, I thought.
And the next time was not long in coming. The summer and autumn of 2003 turned out to be so fruitful that all speculation about the degeneration of the boletus can be safely sent to the dustbin of opinions. The birch trees went in June and went and went and went without a break until the beginning of October. The field, overgrown with young birches, was completely trampled down by mushroom pickers - but not a single good person returned without a bag of these boletus. The forest edges seemed to be cluttered with stools. Three times in a row (without missing a day) I could not get to the place where I was supposed to meet, my character let me down: I immediately grabbed all the young and strong boletus trees that I only saw, and after 100 meters my trip ended: there was no corny container . I am sure that for many years the 2003 season will be remembered as a fairy tale, but then the sensations were different. It seemed that literally in front of my eyes there was a devaluation of the value of the boletus.
Boletus is famous not only for its pleasant taste, but also for its beneficial properties. Mushroom dishes are prepared simply, but they turn out incredibly tasty.
Boletus is famous not only for its pleasant taste, but also for its beneficial properties.
This is one of the most common and valuable mushrooms that can be found on the territory of Russia and the CIS countries. It belongs to the genus Lekcinum (another name is Obabok) of the Boletov family (famous representatives are boletus mushrooms), which include aspen mushrooms.
These are rather large mushrooms (up to 20 cm in diameter of the cap) with well-defined parts - the stem and the cap. The hat is round, prostrate or hemispherical, has no gloss, pleasant to the touch (velvet). Its color varies greatly: from light milky to dark brown, gray and even black. The older the boletus, the darker it is. The leg is straight, but slightly thickens near the mycelium. Contrasting scales are noticeable on it: white or black.
Grow fast enough(up to 3-4 cm per day), the most precocious by the 6th day reach their maximum length. After the pulp becomes more watery, mucus appears, which becomes an excellent bait for worms. After another 4-5 days, the fungus dies.
In the people, the mushroom is called boletus, birch, obabok or blackhead.
 Boletus is one of the most common and valuable mushrooms that can be found on the territory of Russia and the CIS countries.
Boletus is one of the most common and valuable mushrooms that can be found on the territory of Russia and the CIS countries. Where does the boletus grow
As you can see by the name, which the fungus received for good reason, it forms mycorrhiza with birches, therefore it is often found near them. Almost all species love bright places open to the sun. Appears in June after cherry blossoms, disappears in October or November.
It prefers forest-steppe zones, but feels good even in the tundra next to dwarf birches. Such individuals are jokingly called birch trees, because they are often much higher than these plants.
Boletus boletus are widespread on almost all continents: Eurasia and both Americas.
Where and how to collect boletus (video)
Edible types of boletus
All species of the genus Leccinum are edible, they differ slightly in their taste. They can be consumed raw, fried, dried, boiled or pickled, or frozen for the winter.
In total, there are about 40 species of boletus, but The following can be found throughout the country:
- Ordinary;
- pinking;
- marsh;
- multi-colored;
- black;
- harsh.
 Common boletus
Common boletus Common boletus
The most common type. It has a delicate and pleasant taste. You can distinguish it by a reddish hat with a brown tint. The gray leg is compacted, has a clear thickening at the bottom.
rosy boletus
Unlike its “brothers”, the cut of which darkens over time, this obabok acquires an unusual brick-pink hue. More common in swampy areas. You can recognize it by its characteristic low leg, which sharply bends to the side.
swamp boletus
Prefers moist soil and dark places. The color of the mushroom is light, the flesh is loose, it breaks well.
 Black boletus
Black boletus Birch multi-colored
Very beautiful representative, famous for his unique color. Hat of non-uniform color: dark base with white and beige stains, covered with yellow, orange, brick or grayish spots.
Black boletus
Rare mushroom. It is difficult to find it, it is a real success even for an experienced mushroom picker, because a dish made from them will be remembered even by those who do not like “forest bread”. The brown, bluish-black cap is noticeable from afar, the leg is almost completely covered with dark blotches.
Boletus harsh
The sweet and fragrant mushroom is quite tough, but after processing it becomes pleasant in texture. Thanks to the purplish-brown hat, obabok is difficult to confuse with other species. The thick stalk is smooth in old specimens, and strongly scaly in young ones.
 Boletus belongs to the second mushroom category
Boletus belongs to the second mushroom category Useful properties and taste of boletus
It is known that the mushroom was collected in the times of Ancient Russia, it was actively used for food and harvested for future use. But most often the blackhead was mixed with other mushrooms (porcini, mushrooms or russula), as it was believed that they did not have a pronounced taste. But today gourmets believe that this is one of the most valuable representatives of "forest bread", it just needs to be cooked correctly. But so far, the boletus belongs to the second mushroom category.
Its useful qualities are amazing:
- Fiber (of which a quarter consists of birch) helps to cleanse the body.
- Normalizes blood sugar levels, reduces glucose.
- Treats kidney disease.
- Calms the nervous system, helps to overcome insomnia.
- Suitable for cancer prevention.
- Useful for mucous membranes and maintaining good skin condition.
- Improves the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, joints and spine.
Its useful to note and low calorie "forest bread" and a high content of vitamins, micro and macro elements necessary for the normal functioning of the body. Therefore, boletus can be used by people who limit their diet, wanting to lose weight.
 Boletes are widespread on almost all continents.
Boletes are widespread on almost all continents. What does a false boletus look like
Mushroom picking is often referred to as silent hunting. And indeed, the mushroom picker is looking for his "prey", wanting to find the best. But dangers lie in wait for every hunt, and this process is no exception. It is important not to make a mistake and not confuse an edible mushroom with a poisonous one.
Bile (false) boletus practically does not differ from its tasty counterpart. He successfully imitates obabok, so often even experienced people make mistakes and bring the "liar" home. One small piece of gall can spoil the whole pan of other mushrooms, because heat treatment helps to fully reveal the unpleasant taste. False boletus is not poisonous, however, scientists believe that its pulp contains toxins that can worsen a person's well-being.
- "Imitator" is not eaten by insects, birds and animals, so it can be recognized by its untouched appearance.
- The wet surface of the caps quickly deforms when touched.
- There are no tubular veins at the bottom of the cap.
- The size of the gall fungus often exceeds the usual birch.
- There are no spots on the stem that a real blackhead has (resembling birch colors) and there are thin veins that look like blood vessels.
These signs will help to recognize the false boletus.
 Biliary (false) boletus practically does not differ from its tasty counterpart
Biliary (false) boletus practically does not differ from its tasty counterpart How to cook tasty mushroom boletus
Obabok often darkens during cooking, due to which its taste deteriorates a little, and its appearance becomes unpresentable. Therefore, it is desirable to soak it in a solution with citric acid. Don't keep the mushrooms in the water for more than 20 minutes or their texture will become too watery. After the birch trees, it is necessary to rinse and boil for 40-50 minutes, regularly removing the resulting foam.
Mushrooms in sour cream sauce
The first young mushrooms are especially tasty with tender rustic sour cream.
For the dish you will need:
- Mushrooms - 300-400 gr.;
- sour cream - 5 tbsp. l.;
- flour - 1 tsp;
- salt and spices - to taste.
Cooking steps:
- Cut the birch trees into small pieces.
- Fry them in a pre-heated pan. Wait until the moisture is completely gone. Add the onion to the dried mushrooms immediately.
- Salt the mixture and fry the vegetable until golden brown.
- At this time, dilute sour cream with spices (garlic, paprika, black pepper) and flour.
- Pour the mixture over the mushrooms and simmer for 20 minutes over low heat.
 False boletus is not poisonous
False boletus is not poisonous Omelette
An unusual breakfast diversifies the menu. You will need the following products:
- Boiled mushrooms - 150 gr.;
- eggs - 3 pcs.;
- milk - 2 tablespoons;
- hard cheese - 30-50 gr.
- salt, herbs - to taste.
Let's start cooking:
- Boletus fry for 5-10 minutes.
- Whisk eggs with milk.
- Pour the mixture into the skillet;
- After 3 minutes, cover with a lid and lower the heat.
- Wait until a crust forms on the base of the omelette and the top becomes fluffy.
- Sprinkle with herbs and grated cheese. The dish is especially tasty with croutons.
How to fry boletus (video)
Soup
Soup Ingredients:
- Mushrooms - 450-500 gr.;
- potatoes - 200 gr.;
- carrots - 50-70 gr.;
- onion - 2 small;
- tomato - optional;
- noodles or cereals - optional;
- greens - to taste.
Cooking process:
- Boil the mushrooms in brackish water.
- Add finely chopped vegetables (first potatoes, then tomatoes, followed by onions and carrots).
- Pour in cereal or noodles. The term depends on what exactly you have chosen, pasta can be filled up just before turning it off so that they do not boil soft.
- 10 minutes before stopping cooking, add herbs and spices.
What other mushrooms grow under a birch
Not only boletus grows near birches. This tree loves a lot of mushrooms:
- White;
- flywheel green;
- the breast is wet and aspen;
- Champignon;
- boletus;
- russula;
- raincoat.
It is worth spending a day picking a birch tree to enjoy its taste. But be careful not to pick up the gall fungus.
Post Views: 190