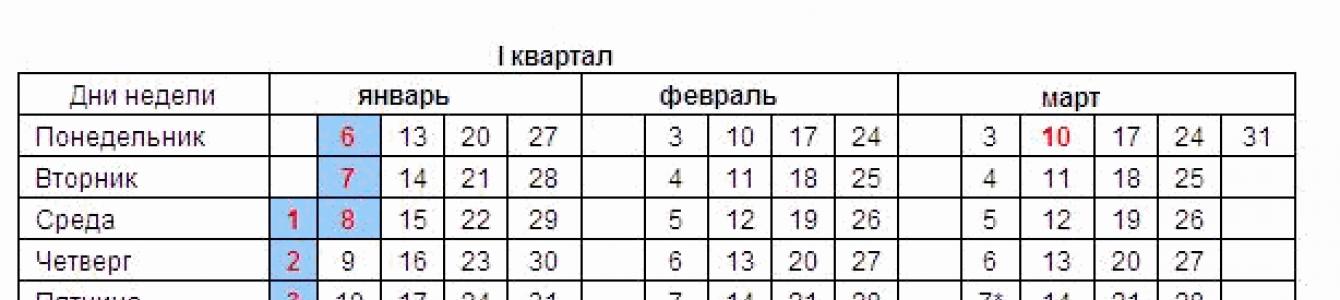
When answering the question, it is necessary to keep in mind that, depending on production conditions, employers can set different lengths of the working week: a five-day work week with two days off, a six-day work week with one day off, etc. (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the general day off is Sunday (Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The production calendar for a six-day period must take into account a number of features. The normal working hours for both a five-day work week and a six-day work week cannot exceed 40 hours per week (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). As a general rule, the standard working time is calculated according to the calculated schedule of a five-day work week with two days off on Saturday and Sunday, based on the duration of daily work (shift): for a 40-hour work week - 8 hours; if the working week is less than 40 hours - the number of hours obtained by dividing the established working week by five days.
With a six-day working week, the standard working time is determined, as a rule, on the basis of a 7-hour working day (Monday to Friday) and a 5-hour working day on Saturday. However, in practice the length of the working day may vary.
2. Part 1 art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the duration of the working day or shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour. This rule applies equally to both a five-day work week and a six-day work week. In addition, according to the Procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods of time (month, quarter, year) depending on the established duration of working time per week (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure), approved. by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated August 13, 2009 No. 588n, in cases where, in accordance with a decision of the Government of the Russian Federation, a day off is transferred to a working day, the duration of work on this day (former day off) must correspond to the duration of the working day to which the day off was transferred. Taking into account the fact that in 2014 the day off on February 24, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 28, 2013 No. 444 “On the transfer of weekends in 2014” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 444), was moved to the working day of November 3 (reduced by one hour), there will be seven such shortened days in 2014: February 22; 24 February; March 7; April 30; May 8; June 11; 31th of December.
3. Part 3 art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation introduces an additional restriction for a six-day working week. According to this norm, on the eve of the weekend, the duration of work in a six-day work week cannot exceed five hours.
4. If a day off coincides with a non-working holiday, the day off is automatically transferred to the next working day after the holiday (Part 2 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, in 2014 there will be only one such transfer: from Sunday, February 23 to Monday, February 24.
Weekends from the number of days off that coincide with the New Year holidays and Christmas (paragraphs 2 and 3 of part 1 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are transferred by the Government of the Russian Federation to other days in the next calendar year. For a six-day working week, Resolution No. 444 provides for one such transfer - the day off January 5 (Sunday) is transferred to June 13 (Friday).
Part 5 Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that for the purpose of rational use by employees of weekends and non-working holidays, weekends may be transferred to other days by federal law or a regulatory legal act of the Government of the Russian Federation.
In 2014, Monday February 24, which became a day off as a result of automatic transfer in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation from Sunday, February 23, was moved by Resolution No. 444 to Monday, November 3.
Thus, in 2014, people working a six-day work week will have a rest from January 1 to January 8 (celebrating the New Year and the Nativity of Christ); from 8 to 9 March (celebration of International Women's Day); from June 12 to June 13 (celebration of Russia Day); from November 2 to November 4 (celebration of National Unity Day).
Let's move on to calculating working hours. In accordance with clause 1 of the Procedure, the standard working time for a particular month is calculated as follows: the length of the working week (40, 39, 36, 30, 24, etc. hours) is divided by 5, multiplied by the number of working days according to the five-day working calendar weeks of a particular month and from the resulting number of hours the number of hours in a given month by which working hours are reduced on the eve of non-working holidays is subtracted.
Personnel Advisor (Tula) informs: How we are relaxing in May 2014, incl. with a 6-hour work week
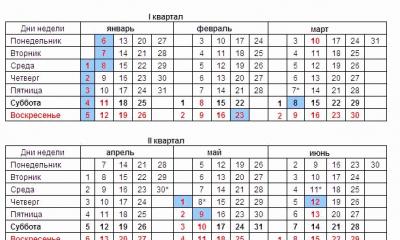
The production calendar presented below shows the norms of established working hours for quarters, months and the year as a whole for 24, 36 and 40-hour work weeks, as well as the number of days off and working days for a five-day work week with two days off and a six-day work week with one day off.
In order to make more rational use of non-working holidays and weekends by workers, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted a resolution to move rest days from Saturday, January 4, to Friday, May 2; from Sunday 5 January to Friday 13 June and from Monday 24 February to Monday 3 November. Additionally, if unplanned changes occur in the future, they will be announced at a later date. It is also worth noting that pre-holiday days, with a forty-hour work week, will
reduced by one hour.
Explanations to the resolution on postponing holidays in 2014
In connection with the above-mentioned transfers of holidays to other days, in May they will last 4 days, including the celebration of Labor Day and Spring. There will also be three days of rest in May, associated with Victory Day.
There will be 4 days off in June (Russia Day) and the same number in November (National Unity Day).
The proposed transfers make it possible to comply with the norm of Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation that there should be at least 42 hours of continuous rest between 2 work weeks.
Non-working days and holidays in 2014
According to Article 112 of the Labor Code of Russia, non-working holidays in 2014 are:
Production calendar for 2014 with a five-day working week
Production calendar for 2014 with a six-day work week
* - Shortened and pre-holiday working days (reduction by 1 hour)
Depending on production conditions, some enterprises and organizations may establish a six-day working week when carrying out activities for their employees (all or certain categories).
This working time regime - a six-day work week with one day off - is applicable under the terms of Art. 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, in accordance with Art. 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the general day off is Sunday.
Normal working hours for both a five-day work week and a six-day work week cannot exceed 40 hours per week. This limitation is established by Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In turn, Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the duration of the working day or shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour. This provision applies equally to both a five-day working week and a six-day working week.
At the same time, this article introduces an additional restriction for a six-day working week, according to which on the eve of weekends the duration of work in this mode cannot exceed five hours.
Labor legislation did not establish the length of working hours for working days when establishing a six-day working week (except Saturday). Therefore, in practice the following operating mode is used:
7 hours + 7 hours + 7 hours + 7 hours + 7 hours + 5 hours = 40 hours per week.
Now let’s see what working and non-working days the 2014 calendar will consist of for workers with a six-day working week.
May 1 and 9 are non-working holidays, Spring and Labor Day and Victory Day, respectively.
The working day on May 8 is shortened by an hour. There will be two holidays, four weekends and 25 working days.
June 12 is a non-working holiday in Russia, June 13 is a day off, moved from January 5, and on June 11, working hours are reduced by one hour.
In June there will be a total of one holiday, six days off and 23 working days.
In July there are four days off and 27 working days.
There are five days off and 26 working days in August.
September
September has four days off and 26 working days.
There are four days off and 27 working days in October.
November 4 is a non-working holiday, National Unity Day, November 3 is a day off, moved from February 24.
November has one holiday, six days off and 23 working days.
In December, the working day on the 31st is shortened by an hour and there will be a total of four days off and 27 working days.
The production calendar presented below shows the norms of established working hours for quarters, months and the year as a whole for 24, 36 and 40-hour work weeks, as well as the number of days off and working days for a five-day work week with two days off and a six-day work week with one day off.
In order to make more rational use of non-working holidays and weekends by workers, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted a resolution to move rest days from Saturday, January 4, to Friday, May 2; from Sunday 5 January to Friday 13 June and from Monday 24 February to Monday 3 November. Additionally, if unplanned changes occur in the future, they will be announced at a later date. It is also worth noting that pre-holiday days, with a forty-hour work week, will be shortened by one hour.
Explanations to the resolution on postponing holidays in 2014
Due to the above transfers of holidays to other days, the winter New Year holiday will be 8 days. In March there will be a 3-day period of "respite" from work, coinciding with International Women's Day. In May it will last 4 days, including the celebration of Labor Day and Spring. There will also be three days of rest in May, associated with Victory Day. There will be 4 days off in June (Russia Day) and the same number in November (National Unity Day).
Such transfers are connected primarily with the aim of eliminating the situation of their transfer in the current order on the eve of the relevant holidays, as well as for the purpose of rational planning of working time at enterprises and taking into account the interests of Russian citizens in organizing leisure time and creating the conditions necessary for proper rest, not only in winter period, but also in spring. The proposed transfers make it possible to comply with the norm of Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation that there should be at least 42 hours of continuous rest between 2 work weeks.
Non-working days and holidays in 2014
According to Article 112 of the Labor Code of Russia, non-working holidays in 2014 are:
Production calendar for 2014 with a five-day working week
Production calendar for 2014 with a six-day work week
* - Shortened and pre-holiday working days (reduction by 1 hour)
Working time standards for 2014

The standard working time for a forty-hour work week in 2014 will be 1971 hours;
The average monthly number of working hours in 2014 was 164.25 hours;
With a five-day working week according to the production calendar in 2014, there will be 247 working days, including five shortened ones (December 31, June 11, May 8, April 30 and March 7) and 118 days off, taking into account four additional days of rest (November 3 , June 13, May 2 and March 10).
When answering the question, it is necessary to keep in mind that, depending on production conditions, employers can set different lengths of the working week: a five-day work week with two days off, a six-day work week with one day off, etc. (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the general day off is Sunday (Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When drawing up a production calendar for a six-day period, it is necessary to take into account a number of features.
1. The normal working hours for both a five-day work week and a six-day work week cannot exceed 40 hours per week (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). As a general rule, the standard working time is calculated according to the calculated schedule of a five-day work week with two days off on Saturday and Sunday, based on the duration of daily work (shift): for a 40-hour work week - 8 hours; if the working week is less than 40 hours - the number of hours obtained by dividing the established working week by five days.
With a six-day working week, the standard working time is determined, as a rule, on the basis of a 7-hour working day (Monday to Friday) and a 5-hour working day on Saturday. However, in practice the length of the working day may vary.
2. Part 1 art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the duration of the working day or shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour. This rule applies equally to both a five-day work week and a six-day work week. In addition, according to the Procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods of time (month, quarter, year) depending on the established duration of working time per week (hereinafter referred to as the Procedure), approved. By order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated August 13, 2009 No. 588n, in cases where, in accordance with a decision of the Government of the Russian Federation, a day off is transferred to a working day, the duration of work on this day (former day off) must correspond to the duration of the working day to which the day off was transferred. Taking into account the fact that in 2014 the day off on February 24, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 28, 2013 No. 444 “On the transfer of weekends in 2014” (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 444), was moved to the working day of November 3 (reduced by one hour), there will be seven such shortened days in 2014: February 22; 24 February; March 7; April 30; May 8; June 11; 31th of December.
3. Part 3 art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation introduces an additional restriction for a six-day working week. According to this norm, on the eve of the weekend, the duration of work in a six-day work week cannot exceed five hours.
4. If a day off coincides with a non-working holiday, the day off is automatically transferred to the next working day after the holiday (Part 2 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, in 2014 there will be only one such transfer: from Sunday, February 23 to Monday, February 24.
Weekends from the number of days off that coincide with the New Year holidays and Christmas (paragraphs 2 and 3 of part 1 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are transferred by the Government of the Russian Federation to other days in the next calendar year. For a six-day working week, Resolution No. 444 provides for one such transfer - the day off January 5 (Sunday) is transferred to June 13 (Friday).
Part 5 Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that for the purpose of rational use by employees of weekends and non-working holidays, weekends may be transferred to other days by federal law or a regulatory legal act of the Government of the Russian Federation.
In 2014, Monday February 24, which became a day off as a result of automatic transfer in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation from Sunday, February 23, was moved by Resolution No. 444 to Monday, November 3.
Thus, in 2014, people working a six-day work week will have a rest from January 1 to January 8 (celebrating the New Year and the Nativity of Christ); from 8 to 9 March (celebration of International Women's Day); from June 12 to June 13 (celebration of Russia Day); from November 2 to November 4 (celebration of National Unity Day).
Let's move on to calculating working hours. In accordance with clause 1 of the Procedure, the standard working time for a particular month is calculated as follows: the length of the working week (40, 39, 36, 30, 24, etc. hours) is divided by 5, multiplied by the number of working days according to the five-day working calendar weeks of a particular month and from the resulting number of hours the number of hours in a given month by which working hours are reduced on the eve of non-working holidays is subtracted.
The standard working time for the year as a whole is calculated in a similar manner: the length of the working week (40, 39, 36, 30, 24, etc. hours) is divided by 5, multiplied by the number of working days according to the calendar of a five-day working week per year and from from the resulting number of hours, the number of hours in a given year by which working hours are reduced on the eve of non-working holidays is subtracted.
The standard working time calculated in the specified Procedure applies to all modes of work and rest.
For example, in January 2014, with a five-day work week with two days off, there were 17 working days and 14 days off. The standard working hours this month, both for a five-day and a six-day working week, are:
with a 40-hour work week – 136 hours (8 hours x 17 days);
with a 36-hour work week – 122.4 hours (7.2 hours x 17 days);
with a 24-hour work week – 81.6 hours (4.8 hours x 17 days).
In February 2014, with a five-day work week with two days off, there were 20 working days (including the working day shortened by one hour on February 24) and 8 days off. With a six-day working week, there will be two shortened working days - February 22 and 24, as a result, the standard working time for this month with a six-day work week will be:
with a 40-hour work week – 158 hours (8 hours x 20 days – 2 hours);
with a 36-hour work week – 142 hours (7.2 hours x 20 days – 2 hours);
with a 24-hour work week – 94 hours (4.8 hours x 20 days – 2 hours).
In May 2014, with a five-day work week with two days off, there were 19 working days (including a working day shortened by one hour on May 8) and 12 days off. The standard working hours this month, both for a five-day and a six-day working week, will be:
with a 40-hour work week – 151 hours (8 hours x 19 days – 1 hour);
with a 36-hour work week – 135.8 hours (7.2 hours x 19 days – 1 hour);
with a 24-hour work week – 90.2 hours (4.8 hours x 19 days – 1 hour).
Thus, in 2014, with a six-day working week, 299 working days (with a five-day working week - 247 working days), including seven working days shortened by one hour (February 22, February 24, March 7, April 30, 8 May, June 11, December 31), and 66 days off, taking into account two additional days of rest: June 13 (due to the coincidence of the non-working holiday on January 5 with a day off) and November 3 (due to the postponement of the day off from February 24) .
Taking into account the above, the standard working time in 2014 for a six-day working week is:
- with a 24-hour work week – 1178.6 hours (4.8 hours x 247 days – 7 hours).
with a 40-hour work week – 1969 hours (8 hours x 247 days – 7 hours);
with a 36-hour work week – 1771.4 hours (7.2 hours x 247 days – 7 hours);
Why do you need a production calendar for 2018 with a six-day working week? How many working days are there in 2018 with a six-day week? What is the standard working time in this mode of operation in 2018? You can view the production calendar in this article.
General information about the production calendar
There are 365 calendar days in 2018. However, there are quite a few holidays in Russia. They also include weekends (with a six-day work week - Sunday). How not to get confused and correctly distribute working time norms during the “six-day work week”? Moreover, if we are talking about accounting, then working days, holidays and weekends must be taken into account when calculating vacation pay, travel allowances and when preparing reports. For this purpose, the production calendar for 2018 is being formed with a six-day working week.
Making a calendar for 2018
Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines non-working holidays, and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 14, 2017 No. 1250 “On the transfer of holidays in 2018”. These regulatory legal acts are the basis for the formation of the production calendar for 2018 with weekends and holidays.
What does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation say about non-working days?
Non-working holidays in the Russian Federation are:
- January 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 – New Year;
- January 7 – Christmas;
- February 23 – Defender of the Fatherland Day;
- March 8 – International Women's Day;
- May 1 – Spring and Labor Day;
- May 9 – Victory Day;
- June 12 – Russia Day;
- November 4 is National Unity Day.
This list of non-working holidays is fixed and does not change from year to year. It is enshrined in Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What transfers to 2018 do not apply to the six-day period?
Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides that the transfer of days off is carried out for the purpose of rational planning of working time in organizations and taking into account the interests of various categories of citizens of the Russian Federation in creating conditions for proper rest. For these purposes, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 14, 2017 No. 1250 “On the transfer of weekends in 2018” provides for the following shift of weekends:
Read also What is the maximum pension in Russia in 2018?
Thus, the following weekends have been moved to 2018:
- Saturday 6 January to Friday 9 March;
- Sunday 7 January to Wednesday 2 May.
- Also, to optimize rest time, weekends have been swapped with working days (Saturdays will be working days, and Mondays will be days off):
- Saturday 28 April to Monday 30 April;
- Saturday 9 June to Monday 11 June;
- Saturday 29 December to Monday 31 December.
In a six-day work week, Saturdays are not days off, which means that these transfers are not provided for a six-day work week.
For those working on a six-day week, March 9, April 30, June 11 and December 31, 2018 will remain working days, since the transfer of days off to these dates is planned from Saturdays that coincide with non-working holidays, and for the “six-day week” Saturday is not a day off.
Due to the postponement of January 7 to May 2, workers with a six-day working week in 2018 will have two consecutive days off for the May holidays - May 1 - 2.
Shortened working days with a reduction in working hours by one hour in 2018 for six-day workers will be February 22, March 7, April 30, May 8, June 11, November 3, December 31.
Production calendar for 2018 with a six-day week
Here is the production calendar for 2018 with a six-day working week:

Below we present a quarterly production calendar for a six-day work week (with weekends and holidays). Taking into account all the transfers, the production calendar for a six-day working week will look like this (pre-holiday days, when the working day is reduced by 1 hour, are marked with an asterisk*).